 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: PCA9545 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

Philips
Semiconductors
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic
and reset
2002 Mar 28
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Product data
Supersedes data of 2001 Nov 08

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2
2002 Mar 28
853-2302 27940
FEATURES
∑
1-of-4 bi-directional translating switches
∑
I
2
C interface logic; compatible with SMBus standards
∑
4 active low interrupt inputs
∑
Active low interrupt output
∑
Active low reset input
∑
2 address pins allowing up to 4 devices on the I
2
C bus
∑
Channel selection via I
2
C bus, in any combination
∑
Power up with all switch channels deselected
∑
Low RDS
ON
switches
∑
Allows voltage level translation between 1.8 V, 2.5 V, 3.3 V and
5 V buses
∑
No glitch on power-up
∑
Supports hot insertion
∑
Low stand-by current
∑
Operating power supply voltage range of 2.3 V to 5.5 V
∑
5 V tolerant Inputs
∑
0 to 400 kHz clock frequency
∑
ESD protection exceeds 2000 V HBM per JESD22-A114,
150 V MM per JESD22-A115 and 1000 V per JESD22-C101
∑
Latch-up testing is done to JESDEC Standard JESD78 which
exceeds 100 mA
∑
Package Offer: SO20, TSSOP20
DESCRIPTION
The PCA9545 is a quad bi-directional translating switch controlled
via the I
2
C bus. The SCL/SDA upstream pair fans out to four
downstream pairs, or channels. Any individual SCx/SDx channel or
combination of channels can be selected, determined by the
contents of the programmable control register. Four interrupt inputs,
INT0 to INT3, one for each of the downstream pairs, are provided.
One interrupt output, INT, acts as an AND of the four interrupt
inputs.
An active-LOW reset input allows the PCA9545 to recover from a
situation where one of the downstream I
2
C buses is stuck in a LOW
state. Pulling the RESET pin LOW resets the I
2
C state machine and
causes all the channels to be deselected as does the internal power
on reset function.
The pass gates of the switches are constructed such that the V
DD
pin can be used to limit the maximum high voltage which will be
passed by the PCA9545. This allows the use of different bus
voltages on each pair, so that 1.8 V or 2.5 V or 3.3 V parts can
communicate with 5 V parts without any additional protection.
External pull-up resistors pull the bus up to the desired voltage level
for each channel. All I/O pins are 5 V tolerant.
PIN CONFIGURATION
A0
A1
RESET
INT0
SD1
V
DD
SDA
SCL
1
20
2
19
3
18
4
17
5
16
6
15
7
14
8
13
SD0
SC0
INT1
INT
SC3
SD3
INT3
SC2
9
12
10
11
SC1
VSS
SD2
INT2
SW00762
Figure 1. Pin configuration
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN
NUMBER
SYMBOL
FUNCTION
1
A0
Address input 0
2
A1
Address input 1
3
RESET
Active low reset input
4
INT0
Active low interrupt input 0
5
SD0
Serial data 0
6
SC0
Serial clock 0
7
INT1
Active low interrupt input 1
8
SD1
Serial data 1
9
SC1
Serial clock 1
10
V
SS
Supply ground
11
INT2
Active low interrupt input 2
12
SD2
Serial data 2
13
SC2
Serial clock 2
14
INT3
Active low interrupt input 3
15
SD3
Serial data 3
16
SC3
Serial clock 3
17
INT
Active low interrupt output
18
SCL
Serial clock line
19
SDA
Serial data line
20
V
DD
Supply voltage
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGES
TEMPERATURE RANGE
ORDER CODE
DRAWING NUMBER
20-Pin Plastic SO
≠40 to +85
∞
C
PCA9545D
SOT163-1
20-Pin Plastic TSSOP
≠40 to +85
∞
C
PCA9545PW
SOT360-1
Standard packing quantities and other packaging data is available at www.philipslogic.com/packaging.

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
3
853-2302 27311
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SW00758
SC0
SC1
SC2
SC3
SD0
SD1
SD2
SD3
V
SS
SCL
V
DD
SDA
INPUT
FILTER
POWER ON
RESET
I
2
C-BUS
CONTROL
A0
INT[0≠3]
INT LOGIC
INT
A1
RESET
PCA9545
SWITCH CONTROL LOGIC
Figure 2. Block diagram

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
4
853-2302 27311
DEVICE ADDRESS
Following a START condition the bus master must output the
address of the slave it is accessing. The address of the PCA9545 is
shown in Figure 3. To conserve power, no internal pullup resistors
are incorporated on the hardware selectable address pins and they
must be pulled HIGH or LOW.
A1 A0
0
0
SW00893
1
1
1
R/W
FIXED
HARDWARE SELECTABLE
Figure 3. Slave address
The last bit of the slave address defines the operation to be
performed. When set to logic 1, a read is selected while a logic 0
selects a write operation.
CONTROL REGISTER
Following the successful acknowledgement of the slave address,
the bus master will send a byte to the PCA9545, which will be stored
in the control register. If multiple bytes are received by the
PCA9545, it will save the last byte received. This register can be
written and read via the I
2
C bus.
SW00949
CHANNEL SELECTION BITS
INTERRUPT BITS
(READ ONLY)
(READ/WRITE)
6
5
4
2
1
0
7
3
CHANNEL 0
CHANNEL 1
CHANNEL 2
CHANNEL 3
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
INT3 INT2 INT1 INT0
B3
B2
B1
B0
Figure 4. Control Register
CONTROL REGISTER DEFINITION
One or several SCx/SDx downstream pair, or channel, is selected
by the contents of the control register. This register is written after
the PCA9545 has been addressed. The 2 LSBs of the control byte
are used to determine which channel is to be selected. When a
channel is selected, the channel will become active after a stop
condition has been placed on the I
2
C bus. This ensures that all
SCx/SDx lines will be in a HIGH state when the channel is made
active, so that no false conditions are generated at the time of
connection.
Table 1. Control Register; Write -- Channel Selection/
Read -- Channel Status
INT3
INT2
INT1
INT0
B3
B2
B1
B0
COMMAND
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
0
Channel 0
disabled
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
Channel 0
enabled
X
X
X
X
X
X
0
X
Channel 1
disabled
X
X
X
X
X
X
1
X
Channel 1
enabled
X
X
X
X
X
0
X
X
Channel 2
disabled
X
X
X
X
X
1
X
X
Channel 2
enabled
X
X
X
X
0
X
X
X
Channel 3
disabled
X
X
X
X
1
X
X
X
Channel 3
enabled
NOTE: Several channels can be enabled at the same time.
Ex: B3 = 0, B2 = 1, B1 = 1, B0 = 0, means that channel 0 and 3 are
disabled and channel 1 and 2 are enabled.
Care should be taken not to exceed the maximum bus capacity.

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
5
853-2302 27311
INTERRUPT HANDLING
The PCA9545 provides 4 interrupt inputs, one for each channel, and
one open drain interrupt output. When an interrupt is generated by any
device, it will be detected by the PCA9545 and the interrupt output
will be driven LOW. The channel does not need to be active for
detection of the interrupt. A bit is also set in the control register.
Bits 4 ≠ 7 of the control register correspond to channels 0 ≠ 3 of the
PCA9545, respectively. Therefore, if an interrupt is generated by any
device connected to channel 1, the state of the interrupt inputs is
loaded into the control register when a read is accomplished.
Likewise, an interrupt on any device connected to channel 0 would
cause bit 4 of the control register to be set on the read. The master
can then address the PCA9545 and read the contents of the control
register to determine which channel contains the device generating the
interrupt. The master can then reconfigure the PCA9545 to select this
channel, and locate the device generating the interrupt and clear it.
It should be noted that more than one device can be providing an
interrupt on a channel, so it is up to the master to ensure that all
devices on a channel are interrogated for an interrupt.
The interrupt inputs may be used as general purpose inputs if the
interrupt function is not required.
If unused, interrupt input(s) must be connected to V
DD
through a
pull-up resistor.
Table 2. Control Register Read -- Interrupt
INT3
INT2
INT1
INT0
B3
B2
B1
B0
COMMAND
X
X
X
0
X
X
X
X
No interrupt
on channel 0
X
X
X
1
X
X
X
X
Interrupt on
channel 0
X
X
0
X
X
X
X
X
No interrupt
on channel 1
X
X
1
X
X
X
X
X
Interrupt on
channel 1
X
0
X
X
X
X
X
X
No interrupt
on channel 2
X
1
X
X
X
X
X
X
Interrupt on
channel 2
0
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
No interrupt
on channel 3
1
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Interrupt on
channel 3
NOTE: Several interrupts can be active at the same time.
Ex: INT3 = 0, INT2 = 1, INT1 = 1, INT0 = 0, means that there is no
interrupt on channels 0 and 3, and there is interrupt on channels 1
and 2.
RESET INPUT
The RESET input is an active-LOW signal which may be used to
recover from a bus fault condition. By asserting this signal LOW for
a minimum of t
WL
, the PCA9545 will reset its registers and I
2
C state
machine and will deselect all channels. The RESET input must be
connected to V
DD
through a pull-up resistor.
POWER-ON RESET
When power is applied to V
DD
, an internal Power On Reset holds
the PCA9545 in a reset state until V
DD
has reached V
POR
. At this
point, the reset condition is released and the PCA9545 registers and
I
2
C state machine are initialized to their default states, all zeroes
causing all the channels to be deselected.
VOLTAGE TRANSLATION
The pass gate transistors of the PCA9545 are constructed such that
the V
DD
voltage can be used to limit the maximum voltage that will
be passed from one I
2
C bus to another.
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
V
pass
vs. V
DD
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
V
pass
V
DD
MINIMUM
TYPICAL
MAXIMUM
SW00820
2.0
Figure 5. V
pass
voltage vs. V
DD
Figure 5 shows the voltage characteristics of the pass gate
transistors (note that the graph was generated using the data
specified in the DC Characteristics section of this datasheet). In
order for the PCA9545 to act as a voltage translator, the V
pass
voltage should be equal to, or lower than the lowest bus voltage. For
example, if the main bus was running at 5 V, and the downstream
buses were 3.3 V and 2.7 V, then V
pass
should be equal to or below
2.7 V to effectively clamp the downstream bus voltages. Looking at
Figure 5, we see that V
pass
(max.) will be at 2.7 V when the
PCA9545 supply voltage is 3.5 V or lower so the PCA9545 supply
voltage could be set to 3.3 V. Pull-up resistors can then be used to
bring the bus voltages to their appropriate levels (see Figure 12).
More Information can be found in Application Note AN262
PCA954X
family of I
2
C/SMBus multiplexers and switches.

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
6
853-2302 27311
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I
2
C-BUS
The I
2
C-bus is for 2-way, 2-line communication between different ICs
or modules. The two lines are a serial data line (SDA) and a serial
clock line (SCL). Both lines must be connected to a positive supply
via a pull-up resistor when connected to the output stages of a device.
Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
Bit transfer
One data bit is transferred during each clock pulse. The data on the
SDA line must remain stable during the HIGH period of the clock
pulse as changes in the data line at this time will be interpreted as
control signals (see Figure 6).
SDA
SCL
SW00363
data line
stable;
data valid
change
of data
allowed
Figure 6. Bit transfer
Start and stop conditions
Both data and clock lines remain HIGH when the bus is not busy. A
HIGH-to-LOW transition of the data line, while the clock is HIGH is
defined as the start condition (S). A LOW-to-HIGH transition of the
data line while the clock is HIGH is defined as the stop condition (P)
(see Figure 7).
System configuration
A device generating a message is a `transmitter', a device receiving
is the `receiver'. The device that controls the message is the
`master' and the devices which are controlled by the master are the
`slaves' (see Figure 8).
SDA
SCL
SW00365
S
P
SDA
SCL
START condition
STOP condition
Figure 7. Definition of start and stop conditions
MASTER
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
SLAVE
RECEIVER
SLAVE
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
MASTER
TRANSMITTER
MASTER
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
SDA
SCL
SW00366
I
2
C
MULTIPLEXER
SLAVE
Figure 8. System configuration

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
7
853-2302 27311
Acknowledge
The number of data bytes transferred between the start and the stop conditions from transmitter to receiver is not limited. Each byte of eight bits
is followed by one acknowledge bit. The acknowledge bit is a HIGH level put on the bus by the transmitter whereas the master generates an
extra acknowledge related clock pulse.
A slave receiver which is addressed must generate an acknowledge after the reception of each byte. Also a master must generate an
acknowledge after the reception of each byte that has been clocked out of the slave transmitter. The device that acknowledges has to pull down
the SDA line during the acknowledge clock pulse, so that the SDA line is stable LOW during the HIGH period of the acknowledge related clock
pulse, set-up and hold times must be taken into account.
A master receiver must signal an end of data to the transmitter by not generating an acknowledge on the last byte that has been clocked out of
the slave. In this event, the transmitter must leave the data line HIGH to enable the master to generate a stop condition.
DATA OUTPUT
BY TRANSMITTER
SCL FROM
MASTER
SW00368
DATA OUTPUT
BY RECEIVER
1
2
8
9
S
START condition
clock pulse for
acknowledgement
acknowledge
not acknowledge
Figure 9. Acknowledgement on the I
2
C-bus
Bus transactions
Data is transmitted to the PCA9545 control register using the write mode as shown in Figure 10.
S
SDA
0
A
A
1
1
1
0
0
A1
A0
SLAVE ADDRESS
start condition
R/W
acknowledge
from slave
acknowledge
from slave
B0
CONTROL REGISTER
X
P
SW00760
B1
X
B2
X
B3
X
stop condition
Figure 10. WRITE control register
Data is read from PCA9545 control register using the read mode as shown in Figure 11.
SDA
S
1
A
NA
1
1
1
0
0
A1 A0
start condition
R/W
acknowledge
from slave
CONTROL REGISTER
P
stop condition
last byte
SW00761
SLAVE ADDRESS
no acknowledge
from master
B0
INT0
B1
INT1
B2
INT2
B3
INT3
Figure 11. READ control register

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
8
853-2302 27311
TYPICAL APPLICATION
PCA9545
V = 2.7 ≠ 5.5 V
SD0
SC0
V = 2.7 ≠ 5.5 V
SD1
SC1
A1
A0
V
SS
SDA
SCL
RESET
V
DD
= 3.3 V
V
DD
= 2.7 ≠ 5.5 V
I
2
C/SMBus MASTER
SW00810
SDA
SCL
CHANNEL 0
CHANNEL 1
V = 2.7 ≠ 5.5 V
SD2
SC2
CHANNEL 2
V = 2.7 ≠ 5.5 V
SD3
SC3
CHANNEL 3
INT
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
NOTE:
1.
If the device generating the Interrupt has an open-drain output structure or
can be tri-stated, a pull-up resistor is required.
If the device generating the Interrupt has a totem-pole output structure and
cannot be tri-stated, a pull-up resistor is not required.
The Interrupt inputs should not be left floating.
SEE NOTE (1)
SEE NOTE (1)
SEE NOTE (1)
SEE NOTE (1)
Figure 12. Typical application
Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
9
853-2302 27311
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1, 2
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).Voltages are referenced to GND (ground = 0 V).
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
RATING
UNIT
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN
MAX
UNIT
V
DD
DC supply voltage
≠0.5
+7.0
V
V
I
DC input voltage
≠0.5
+7.0
V
I
I
DC input current
--
±
20
mA
I
O
DC output current
--
±
25
mA
I
DD
DC Supply current
--
±
100
mA
I
SS
DC Supply current
--
±
100
mA
P
tot
total power dissipation
--
400
mW
T
stg
Storage temperature range
≠60
+150
∞
C
T
amb
Operating ambient temperature
≠40
+85
∞
C
NOTES:
1. Stresses beyond those listed may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating conditions" is not implied. Exposure to
absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2. The performance capability of a high-performance integrated circuit in conjunction with its thermal environment can create junction
temperatures which are detrimental to reliability. The maximum junction temperature of this integrated circuit should not exceed 150
∞
C.
DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
DD
= 2.3 to 3.6 V; V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= ≠40 to +85
∞
C; unless otherwise specified. (See page 11 for V
DD
= 3.6 to 5.5 V.)
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
LIMITS
UNIT
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Supply
V
DD
Supply voltage
2.3
--
3.6
V
I
DD
Supply current
Operating mode; V
DD
= 3.6 V;
no load; V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
;
f
SCL
= 100 kHz
--
30
100
µ
A
I
stb
Standby current
Standby mode; V
DD
= 3.6 V;
no load; V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
--
20
100
µ
A
V
POR
Power-on reset voltage
no load; V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
--
1.6
2.1
V
Input SCL; input/output SDA
V
IL
LOW level input voltage
≠0.5
--
0.3 V
DD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage
0.7 V
DD
--
6
V
I
OL
LOW level output current
V
OL
= 0.4 V
3
--
--
mA
I
OL
LOW level out ut current
V
OL
= 0.6 V
6
--
--
mA
I
L
Leakage current
V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
≠1
--
+1
µ
A
C
i
Input capacitance
V
I
= V
SS
--
12
13
pF
Select inputs A0 to A1 / INT0 to INT3 / RESET
V
IL
LOW level input voltage
≠0.5
--
+0.3 V
DD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage
0.7 V
DD
--
V
DD
+ 0.5
V
I
LI
Input leakage current
pin at V
DD
or V
SS
≠1
--
+1
µ
A
C
i
Input capacitance
V
I
= V
SS
--
1.6
3
pF
Pass Gate
R
ON
Switch resistance
V
DD
= 3.0 to 3.6 V, V
O
= 0.4 V, I
O
= 15 mA
5
20
30
R
ON
Switch resistance
V
DD
= 2.3 to 2.7 V, V
O
= 0.4 V, I
O
= 10 mA
7
26
55
V
swin
= V
DD
= 3.3 V; I
swout
= ≠100
µ
A
--
2.2
--
V
P
Switch output voltage
V
swin
= V
DD
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; I
swout
= ≠100
µ
A
1.6
--
2.8
V
V
Pass
Switch out ut voltage
V
swin
= V
DD
= 2.5 V; I
swout
= ≠100
µ
A
--
1.5
--
V
V
swin
= V
DD
= 2.3 to 2.7 V; I
swout
= ≠100
µ
A
1.1
--
2.0
I
L
Leakage current
V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
≠1
--
+1
µ
A
C
io
Input/output capacitance
V
I
= V
SS
--
3
5
pF
INT Output
I
OL
LOW level output current
V
OL
= 0.4 V
3
--
--
mA
I
OH
HIGH level output current
--
--
+100
µ
A

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
10
853-2302 27311
DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
DD
= 3.6 to 5.5 V; V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= ≠40 to +85
∞
C; unless otherwise specified. (See page 10 for V
DD
= 2.3 to 3.6 V.)
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
LIMITS
UNIT
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Supply
V
DD
Supply voltage
3.6
--
5.5
V
I
DD
Supply current
Operating mode; V
DD
= 5.5 V;
no load; V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
;
f
SCL
= 100 kHz
--
575
600
µ
A
I
stb
Standby current
Standby mode; V
DD
= 5.5 V;
no load; V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
--
130
200
µ
A
V
POR
Power-on reset voltage
no load; V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
--
1.6
2.1
V
Input SCL; input/output SDA
V
IL
LOW level input voltage
≠0.5
--
0.3 V
DD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage
0.7 V
DD
--
6
V
I
OL
LOW level output current
V
OL
= 0.4 V
3
--
--
mA
I
OL
LOW level out ut current
V
OL
= 0.6 V
6
--
--
mA
I
IL
LOW level input current
V
I
= V
SS
≠10
--
+10
µ
A
I
IH
HIGH level input current
V
I
= V
DD
--
--
+100
µ
A
C
i
Input capacitance
V
I
= V
SS
--
12
13
pF
Select inputs A0 to A1 / INT0 to INT3 / RESET
V
IL
LOW level input voltage
≠0.5
--
+0.3 V
DD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage
0.7 V
DD
--
V
DD
+ 0.5
V
I
LI
Input leakage current
pin at V
DD
or V
SS
≠1
--
+50
µ
A
C
i
Input capacitance
V
I
= V
SS
--
1.6
3
pF
Pass Gate
R
ON
Switch resistance
V
CC
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, V
O
= 0.4 V, I
O
= 15 mA
4
11
24
V
P
Switch output voltage
V
swin
= V
DD
= 5.0 V; I
swout
= ≠100
µ
A
--
3.5
--
V
V
Pass
Switch out ut voltage
V
swin
= V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V; I
swout
= ≠100
µ
A
2.6
--
4.5
V
I
L
Leakage current
V
I
= V
DD
or V
SS
≠1
--
+100
µ
A
C
io
Input/output capacitance
V
I
= V
SS
--
3
5
pF
INT Output
I
OL
LOW level output current
V
OL
= 0.4 V
3
--
--
mA
I
OH
HIGH level output current
--
--
+100
µ
A

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
11
853-2302 27311
AC CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
STANDARD-MODE
I
2
C-BUS
FAST-MODE I
2
C-BUS
UNIT
MIN
MAX
MIN
MAX
t
pd
Propagation delay from SDA to SD
n
or SCL to SC
n
--
0.3
1
--
0.3
1
ns
f
SCL
SCL clock frequency
0
100
0
400
kHz
t
BUF
Bus free time between a STOP and START condition
4.7
--
1.3
--
µ
s
t
HD;STA
Hold time (repeated) START condition
After this period, the first clock pulse is generated
4.0
--
0.6
--
µ
s
t
LOW
LOW period of the SCL clock
4.7
--
1.3
--
µ
s
t
HIGH
HIGH period of the SCL clock
4.0
--
0.6
--
µ
s
t
SU;STA
Set-up time for a repeated START condition
4.7
--
0.6
--
µ
s
t
SU;STO
Set-up time for STOP condition
4.0
--
0.6
--
µ
s
t
HD;DAT
Data hold time
0
2
3.45
0
2
0.9
µ
s
t
SU;DAT
Data set-up time
250
--
100
--
ns
t
R
Rise time of both SDA and SCL signals
--
1000
20 + 0.1C
b
3
300
ns
t
F
Fall time of both SDA and SCL signals
--
300
20 + 0.1C
b
3
300
µ
s
C
b
Capacitive load for each bus line
--
400
--
400
µ
s
t
SP
Pulse width of spikes which must be suppressed
by the input filter
--
50
--
50
ns
t
VD:DATL
Data valid (HL)
--
1
--
1
µ
s
t
VD:DATH
Data valid (LH)
--
0.6
--
0.6
µ
s
t
VD:ACK
Data valid Acknowledge
--
1
--
1
µ
s
INT
t
iv
INTn to INT active valid time
--
4
--
4
µ
s
t
ir
INTn to INT inactive delay time
--
2
--
2
µ
s
L
pwr
LOW level pulse width rejection or INTn inputs
1
--
1
--
µ
s
H
pwr
HIGH level pulse width rejection or INTn inputs
0.5
--
0.5
--
µ
s
RESET
t
WL(rst)
Pulse width low reset
4
--
4
--
ns
t
rst
Reset time (SDA clear)
500
--
500
--
ns
t
REC:STA
Recovery to Start
0
--
0
--
ns
NOTES:
1. Pass gate propagation delay is calculated from the 20
typical R
ON
and the 15 pF load capacitance.
2. A device must internally provide a hold time of at least 300 ns for the SDA signal (referred to the VIH
min
of the SCL signal) in order to bridge
the undefined region of the falling edge of SCL.
3. C
b
= total capacitance of one bus line in pF.
t
SP
t
BUF
t
HD;STA
P
P
S
t
LOW
t
R
t
HD;DAT
t
F
t
HIGH
t
SU;DAT
t
SU;STA
Sr
t
HD;STA
t
SU;STO
SDA
SCL
SU00645
Figure 13. Definition of timing on the I
2
C-bus

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
12
853-2302 27311
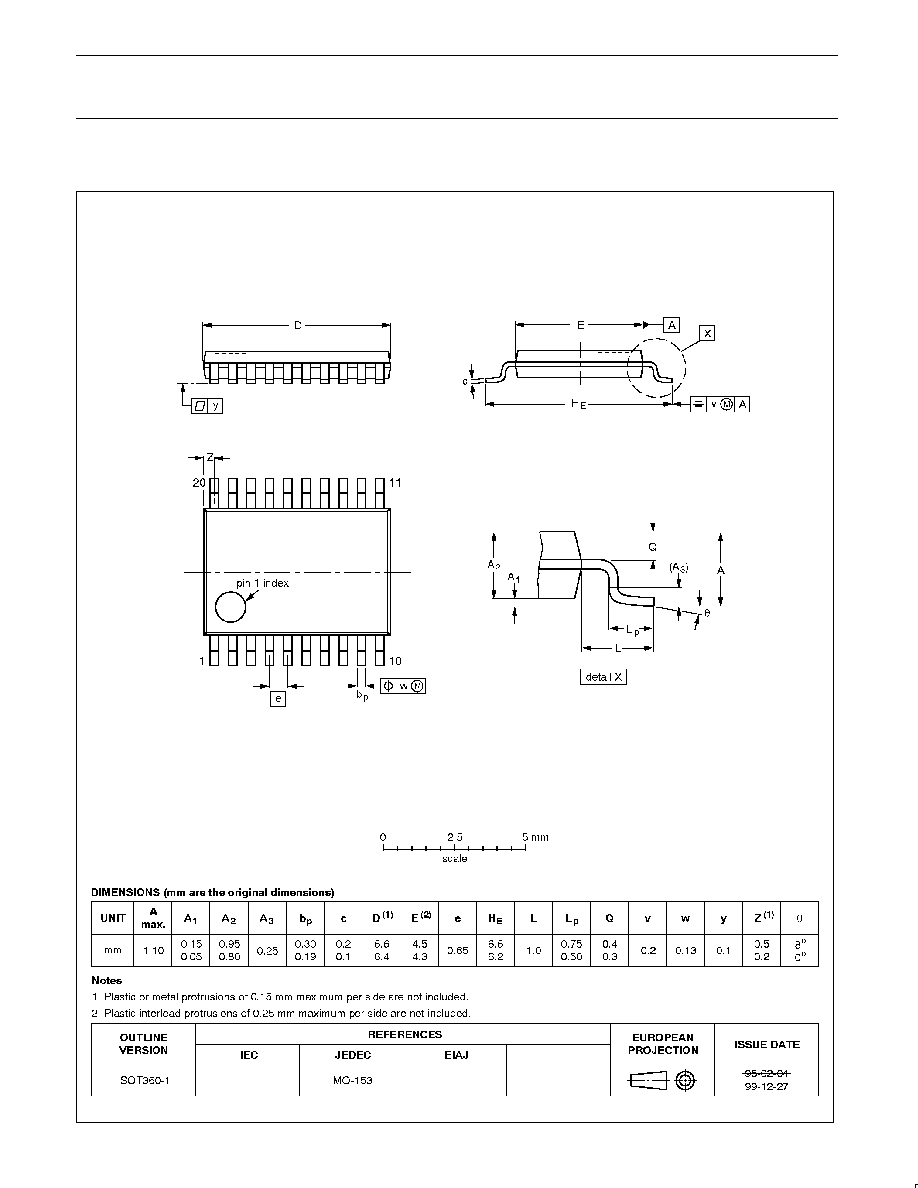
SO20:
plastic small outline package; 20 leads; body width 7.5 mm
SOT163-1
Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
13
853-2302 27311
TSSOP20:
plastic thin shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm
SOT360-1

Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9545
4-channel I
2
C switch with interrupt logic and reset
2002 Mar 28
14
853-2302 27311
Purchase of Philips I
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips' I
2
C patent
to use the components in the I
2
C system provided the system conforms to the
I
2
C specifications defined by Philips. This specification can be ordered using the
code 9398 393 40011.
Definitions
Short-form specification -- The data in a short-form specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the same type number and title. For
detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition -- Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Stress above one
or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or
at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Application information -- Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips
Semiconductors make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
Disclaimers
Life support -- These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips Semiconductors customers using or selling these products for use in such applications
do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes -- Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the products, including circuits, standard
cells, and/or software, described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or performance. Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, and makes no representations or warranties that these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work right infringement, unless
otherwise specified.
Contact information
For additional information please visit
http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to:
sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
©
Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2002
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
Date of release: 03-02
Document order number:
9397 750 09608
Philips
Semiconductors
Data sheet status
[1]
Objective data
Preliminary data
Product data
Product
status
[2]
Development
Qualification
Production
Definitions
This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product development.
Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification in any manner without notice.
This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification. Supplementary data will be
published at a later date. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification
without notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible product.
This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips Semiconductors reserves the
right to make changes at any time in order to improve the design, manufacturing and supply.
Changes will be communicated according to the Customer Product/Process Change Notification
(CPCN) procedure SNW-SQ-650A.
Data sheet status
[1] Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
[2] The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL
http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.













