 | ÐлекÑÑоннÑй компоненÑ: AD8191 | СкаÑаÑÑ:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Äîêóìåíòàöèÿ è îïèñàíèÿ www.docs.chipfind.ru
4:1 HDMI/DVI Switch with Equalization
AD8191
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113
©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
FEATURES
Four inputs, one output HDMITM/DVI links
Four TMDS channels per link
Supports 250 Mbps to 1.65 Gbps data rates
Supports 25 MHz to 165 MHz pixel clocks
Equalized inputs for operation with long HDMI cables
(20 meters at 1080p)
Fully buffered unidirectional inputs/outputs
Globally switchable, 50 on-chip terminations
Pre-emphasized outputs
Low added jitter
Single-supply operation (3.3 V)
Four auxiliary channels per link
Bidirectional unbuffered inputs/outputs
Flexible supply operation (3.3 V to 5 V)
HDCP standard compatible
Allows switching of DDC bus and two additional signals
Multiple channel bundling modes
1x (4:1) HDMI/DVI link switch (default)
2x (8:1) TMDS channel and auxiliary signal switch
1x (16:1) TMDS channel and auxiliary signal switch
Output disable feature
Reduced power dissipation
Removable output termination
Allows building of larger arrays
Two AD8191s support HDMI/DVI dual-link
Standards compatible: HDMI receiver, DVI, HDCP
Serial (I
2
C® slave) and parallel control interface
100-lead, 14 mm × 14 mm LQFP, Pb-free package
APPLICATIONS
Multiple input displays
Projectors
A/V receivers
Set-top boxes
Advanced television (HDTV) sets
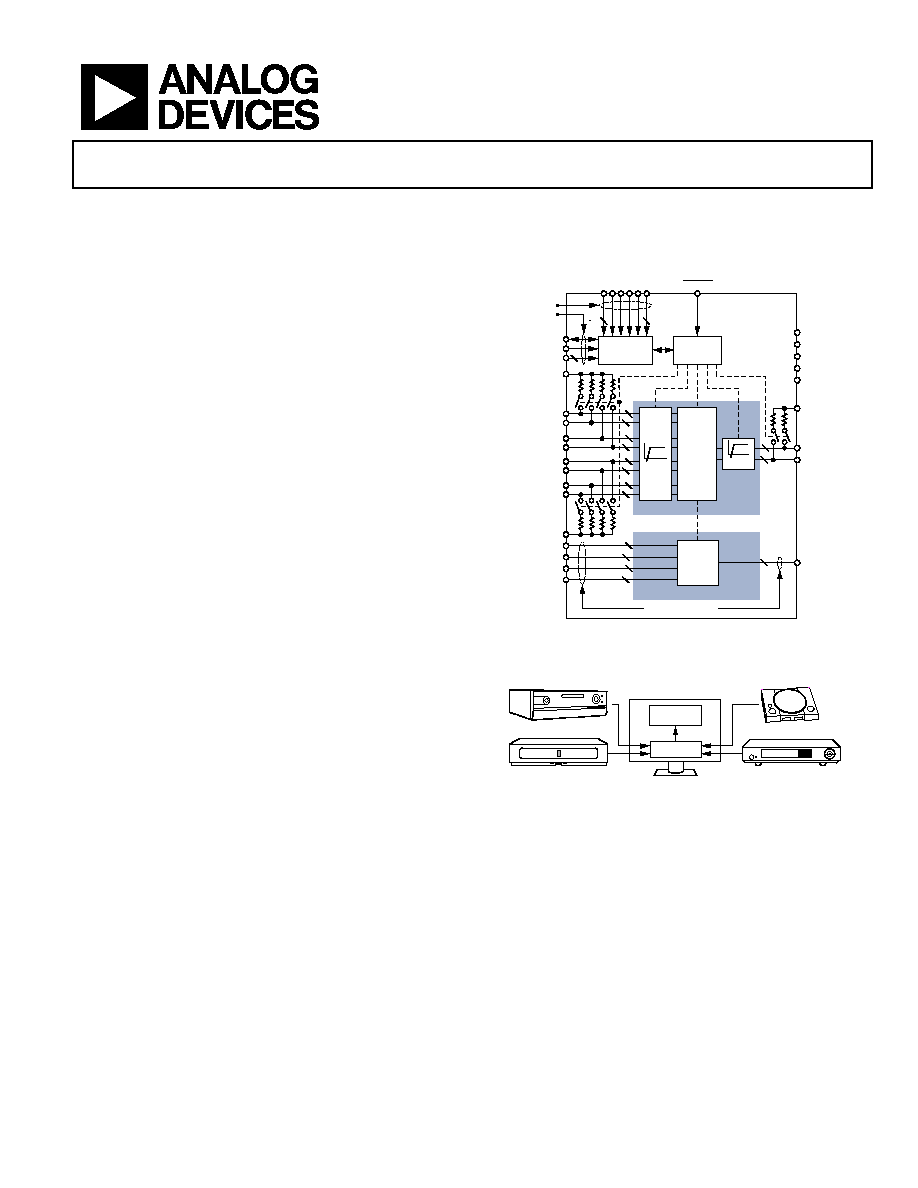
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
LOW SPEED UNBUFFERED
HIGH SPEED
BUFFERED
AVCC
DVCC
AMUXVCC
AVEE
DVEE
VTTO
OP[3:0]
AUX_COM[3:0]
ON[3:0]
+
4
BIDIRECTIONAL
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
I2C_ADDR[2:0]
VTTI
VTTI
IP_A[3:0]
IN_A[3:0]
+
IP_B[3:0]
IN_B[3:0]
+
IP_C[3:0]
IN_C[3:0]
+
IP_D[3:0]
IN_D[3:0]
AUX_C[3:0]
AUX_B[3:0]
AUX_A[3:0]
AUX_D[3:0]
+
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
EQ
SWITCH
CORE
SWITCH
CORE
CONTROL
LOGIC
CONFIG
INTERFACE
3
2
2
SERIAL
PARALLEL
P
P
_C
H[
1:
0
]
PP
_
O
T
O
PP
_
O
CL
PP
_
E
Q
PP
_
E
N
PP
_
P
R
E
[1
:
0
]
RESET
PE
4
4
AD8191
0
612
3-
00
1
Figure 1.
TYPICAL APPLICATION
DVD PLAYER
GAME CONSOLE
SET-TOP BOX
MEDIA CENTER
HDTV SET
HDMI
RECEIVER
AD8191
01:18
0
612
3-
0
02
Figure 2. Typical HDTV Application
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD8191 is a HDMI/DVI switch featuring equalized TMDS
inputs and pre-emphasized TMDS outputs, ideal for systems
with long cable runs. Outputs can be set to a high impedance
state to reduce the power dissipation and/or allow the construc-
tion of larger arrays using the wire-OR technique. Flexible
channel bundling modes (for both the TMDS channels and the
auxiliary signals) allow the AD8191 to be configured as a 4:1 single
HDMI/DVI link switch, a dual 8:1 switch, or a single 16:1 switch.
The AD8191 is provided in a 100-lead LQFP, Pb-free, surface
mount package specified to operate over the -40°C to +85°C
temperature range.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1.
Supports data rates up to 1.65 Gbps, enabling 1080p HDMI
formats and UXGA (1600 × 1200) DVI resolutions.
2.
Input cable equalizer enables use of long cables at the input
(more than 20 meters of 24 AWG cable at 1080p).
3.
Auxiliary switch routes a DDC bus and two additional signals
for a single-chip, HDMI 1.2a receive-compliant solution.

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 32
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Typical Application........................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
Maximum Power Dissipation ..................................................... 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 6
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 9
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 13
Introduction ................................................................................ 13
Input Channels............................................................................ 13
Output Channels ........................................................................ 13
High Speed (TMDS) Switching Modes ................................... 14
Auxiliary Switch.......................................................................... 14
Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switching Modes ................................ 15
Serial Control Interface.................................................................. 16
Reset ............................................................................................. 16
Write Procedure.......................................................................... 16
Read Procedure........................................................................... 17
Parallel Control Interface .............................................................. 18
Serial Interface Configuration Registers ..................................... 19
High Speed Device Modes Register......................................... 19
Auxiliary Device Modes Register............................................. 20
Receiver Settings Register ......................................................... 22
Input Termination Pulse Register 1 and Register 2 ............... 22
Receive Equalizer Register 1 and Register 2 ........................... 22
Transmitter Settings Register.................................................... 22
Parallel Interface Configuration Registers .................................. 23
High Speed Device Modes Register......................................... 23
Auxiliary Device Modes Register............................................. 23
Receiver Settings Register ......................................................... 24
Input Termination Pulse Register 1 and Register 2 ............... 24
Receive Equalizer Register 1 and Register 2 ........................... 24
Transmitter Settings Register.................................................... 24
Application Notes ........................................................................... 25
Pinout........................................................................................... 25
Cable Lengths and Equalization............................................... 25
PCB Layout Guidelines.............................................................. 26
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 30
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 30
REVISION HISTORY
10/06--Revision 0: Initial Version
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 32
SPECIFICATIONS
T
A
= 27°C, AVCC = 3.3 V, VTTI = 3.3 V, VTTO = 3.3 V, DVCC = 3.3 V, AMUXVCC = 5 V, AVEE = 0 V, DVEE = 0 V, differential input
swing = 1000 mV, TMDS outputs terminated with external 50 resistors to 3.3 V, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions/Comments
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Maximum Data Rate (DR) per Channel
NRZ
1.65
Gbps
Bit Error Rate (BER)
PRBS 2
23
- 1
10
-9
Added Deterministic Jitter
DR 1.65 Gbps, PRBS 2
23
- 1
40
ps (p-p)
Added Random Jitter
2
ps (rms)
Differential Intrapair Skew At
output
1
ps
Differential Interpair Skew
1
At output
40
ps
EQUALIZATION PERFORMANCE
Receiver (Highest Setting)
2
Boost frequency = 825 MHz
12
dB
Transmitter (Highest Setting)
3
Boost frequency = 825 MHz
6
dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Voltage Swing
Differential
150
1200
mV
Input Common-Mode Voltage (V
ICM
)
AVCC - 800
AVCC
mV
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
High Voltage Level
Single-ended high speed channel
AVCC - 10
AVCC + 10
mV
Low Voltage Level
Single-ended high speed channel
AVCC - 600
AVCC - 400
mV
Rise/Fall Time (20% to 80%)
75
135
200
ps
INPUT TERMINATION
Resistance Single-ended
50
AUXILIARY CHANNELS
On Resistance, R
AUX
100
On Capacitance, C
AUX
DC bias = 2.5 V, ac voltage = 3.5 V, f = 100 kHz
8
pF
Input/Output Voltage Range
DVEE
AMUXVCC
V
POWER SUPPLY
AVCC Operating
range 3
3.3
3.6
V
QUIESCENT CURRENT
AVCC Outputs
disabled
30
40
44
mA
Outputs enabled, no pre-emphasis
48
60
64
mA
Outputs enabled, maximum pre-emphasis
88
100
110
mA
VTTI
Input termination on
4
5 40
54
mA
VTTO
Output termination on, no pre-emphasis
35
40
46
mA
Output termination on, maximum
pre-emphasis
72 80
90 mA
DVCC
3.2
7
8
mA
AMUXVCC
0.01
0.1
mA
POWER DISSIPATION
Outputs
disabled
115
271
361
mW
Outputs enabled, no pre-emphasis
384
574
671
mW
Outputs enabled, maximum pre-emphasis
704
910
1050
mW
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Switching/Update Delay
High speed switching register: HS_CH
200
ms
All other configuration registers
1.5
ms
RESET Pulse Width
50
ns
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 32
Parameter Conditions/Comments
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
SERIAL CONTROL INTERFACE
5
Input High Voltage, V
IH
2
V
Input Low Voltage, V
IL
0.8
V
Output High Voltage, V
OH
2.4
V
Output Low Voltage, V
OL
0.4
V
PARALLEL CONTROL INTERFACE
Input High Voltage, V
IH
2
V
Input Low Voltage, V
IL
0.8
V
1
Differential interpair skew is measured between the TMDS pairs of a single link.
2
AD8191 output meets the transmitter eye diagram as defined in the DVI Standard Revision 1.0 and the HDMI Standard Revision 1.2a.
3
Cable output meets the receiver eye diagram mask as defined in the DVI Standard Revision 1.0 and the HDMI Standard Revision 1.2a.
4
Typical value assumes only the selected HDMI/DVI link is active with nominal signal swings and that the unselected HDMI/DVI links are deactivated. Minimum and
maximum limits are measured at the respective extremes of input termination resistance and input voltage swing.
5
The AD8191 is an I
2
C slave and its serial control interface is based on the 3.3 V I
2
C bus specification.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 32
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
AVCC to AVEE
3.7 V
DVCC to DVEE
3.7 V
DVEE to AVEE
±0.3 V
VTTI
AVCC + 0.6 V
VTTO
AVCC + 0.6 V
AMUXVCC 5.5
V
Internal Power Dissipation
2.2 W
High Speed Input Voltage
AVCC - 1.4 V < V
IN
<
AVCC + 0.6 V
High Speed Differential Input Voltage
2.0 V
Low Speed Input Voltage
DVEE - 0.3 V < V
IN
<
AMUXVCC + 0.6 V
I
2
C and Parallel Logic Input Voltage
DVEE - 0.3 V < V
IN
<
DVCC + 0.6 V
Storage Temperature Range
-65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature
150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
JA
is specified for the worst-case conditions: a device soldered
in a 4-layer JEDEC circuit board for surface-mount packages.
JC
is specified for no airflow.
Table 3. Thermal Resistance
Package Type
JA
JC
Unit
100-Lead LQFP
56
19
°C/W
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum power that can be safely dissipated by the AD8191
is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature. The
maximum safe junction temperature for plastic encapsulated
devices is determined by the glass transition temperature of the
plastic, approximately 150°C. Temporarily exceeding this limit
may cause a shift in parametric performance due to a change in
the stresses exerted on the die by the package.
Exceeding a junction temperature of 175°C for an extended
period can result in device failure. To ensure proper operation, it
is necessary to observe the maximum power rating as determined
by the coefficients in Table 3.
ESD CAUTION
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 32
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
PP
_
O
T
O
AUX
_A0
AUX
_A1
AUX
_A2
AUX
_A3
DV
E
E
AUX
_B0
AUX
_B1
AUX
_B2
AUX
_B3
AUX
_CO
M
0
AUX
_CO
M
1
AUX
_CO
M
2
AUX
_CO
M
3
AUX
_C0
AUX
_C1
AUX
_C2
AUX
_C3
AM
UX
V
CC
AUX
_D0
AUX
_D1
AUX
_D2
AUX
_D3
PP
_
EQ
PP
_
EN
26
I
2
C_ADDR
0
27
I
2
C
_
A
DDR1
28
I
2
C_ADDR2
29
D
VEE
30
PP_
C
H
0
31
P
P
_CH1
32
DV
CC
33
ON
0
34
OP
0
35
VT
T
O
36
ON
1
37
OP
1
38
DV
C
C
39
ON
2
2
IN_B0
3
IP_B0
4
AVEE
7
VTTI
6
IP_B1
5
IN_B1
1
AVCC
8
IN_B2
9
IP_B2
10
AVEE
12
IP_B3
13
AVCC
14
IN_A0
15
IP_A0
16
AVEE
17
IN_A1
18
IP_A1
19
VTTI
20
IN_A2
21
IP_A2
22
AVCC
23
IN_A3
24
IP_A3
25
AVEE
11
IN_B3
74
IP_C3
AVCC
73
IN_C3
72
AVEE
69
VTTI
70
IN_C2
71
IP_C2
75
68
IP_C1
67
IN_C1
66
AVEE
64
IN_C0
63
AVCC
62
IP_D3
61
IN_D3
60
AVEE
59
IP_D2
58
IN_D2
57
VTTI
56
IP_D1
55
IN_D1
54
AVCC
53
IP_D0
52
IN_D0
51
AVEE
65
IP_C0
40
OP
2
41
VT
T
O
42
ON
3
43
OP
3
44
RE
S
E
T
45
PP_
PR
E0
46
PP_
PR
E1
47
DV
C
C
48
PP
_
O
C
L
49
I2
C
_
S
C
L
50
I2
C
_
S
D
A
10
0
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
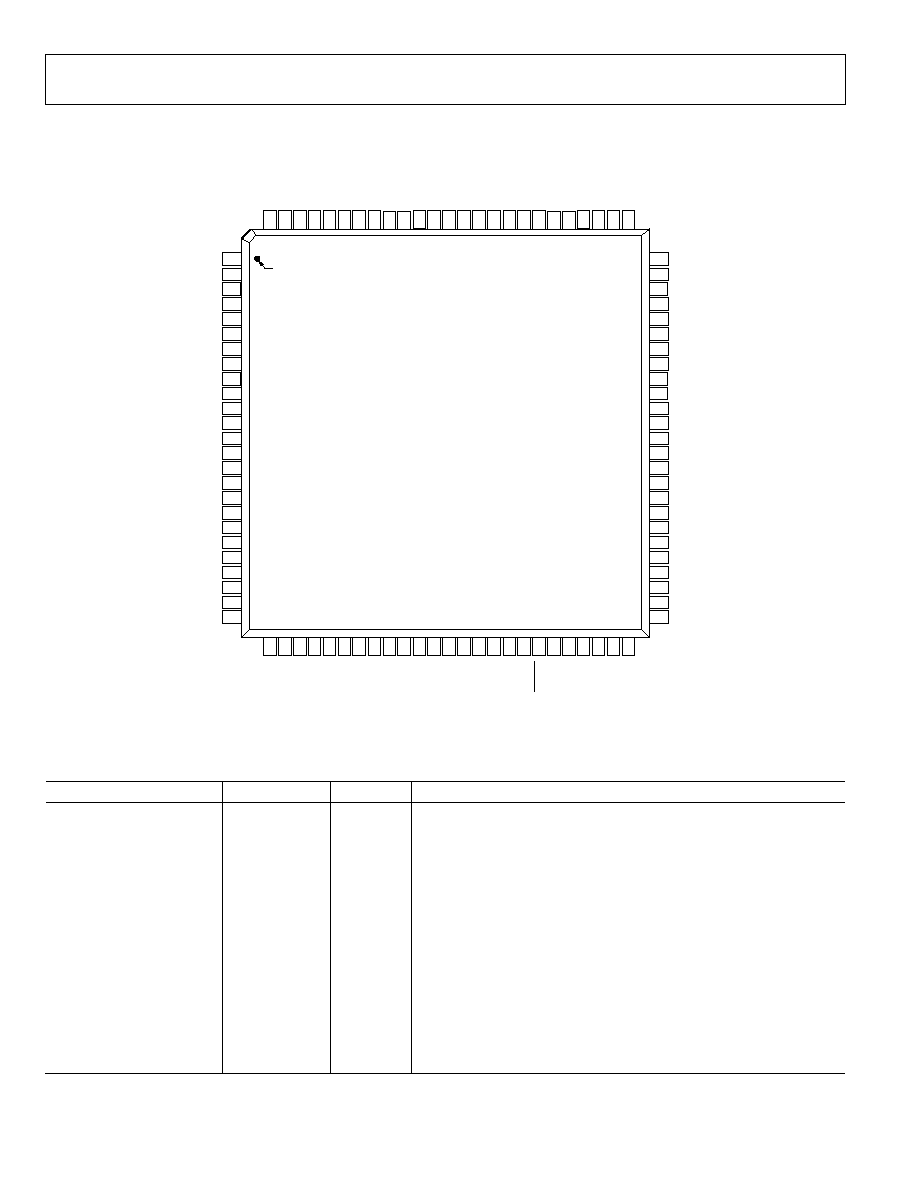
PIN 1 INDICATOR
AD8191
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
0
61
23
-
00
3
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No.
Mnemonic
Type
1
Description
1, 13, 22, 54, 63, 75
AVCC
Power
Positive Analog Supply. 3.3 V nominal.
2
IN_B0
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
3
IP_B0
HS I
High Speed Input.
4, 10, 16, 25, 51, 60, 66, 72
AVEE
Power
Negative Analog Supply. 0 V nominal.
5
IN_B1
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
6
IP_B1
HS I
High Speed Input.
7, 19, 57, 69
VTTI
Power
Input Termination Supply. Nominally connected to AVCC.
8
IN_B2
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
9
IP_B2
HS I
High Speed Input.
11
IN_B3
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
12
IP_B3
HS I
High Speed Input.
14
IN_A0
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
15
IP_A0
HS I
High Speed Input.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 32
Pin No.
Mnemonic
Type
1
Description
17
IN_A1
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
18
IP_A1
HS I
High Speed Input.
20
IN_A2
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
21
IP_A2
HS I
High Speed Input.
23
IN_A3
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
24
IP_A3
HS I
High Speed Input.
26 I2C_ADDR0
Control
I
2
C Address 1
st
LSB.
27 I2C_ADDR1
Control
I
2
C Address 2
nd
LSB.
28 I2C_ADDR2
Control
I
2
C Address 3
rd
LSB.
29, 95
DVEE
Power
Negative Digital and Auxiliary Multiplexer Power Supply. 0 V nominal.
30
PP_CH0
Control
Quad Switching Mode High Speed Source Selection Parallel Interface LSB.
31
PP_CH1
Control
Quad Switching Mode High Speed Source Selection Parallel Interface MSB.
32, 38, 47
DVCC
Power
Positive Digital Power Supply. 3.3 V nominal.
33
ON0
HS O
High Speed Output Complement.
34
OP0
HS O
High Speed Output.
35, 41
VTTO
Power
Output Termination Supply. Nominally connected to AVCC.
36
ON1
HS O
High Speed Output Complement.
37
OP1
HS O
High Speed Output.
39
ON2
HS O
High Speed Output Complement.
40
OP2
HS O
High Speed Output.
42
ON3
HS O
High Speed Output Complement.
43
OP3
HS O
High Speed Output.
44
RESET
Control
Configuration Registers Reset. Normally pulled up to AVCC.
45
PP_PRE0
Control
High Speed Pre-Emphasis Selection Parallel Interface LSB.
46
PP_PRE1
Control
High Speed Pre-Emphasis Selection Parallel Interface MSB.
48
PP_OCL
Control
High Speed Output Current Level Parallel Interface.
49 I2C_SCL
Control
I
2
C Clock.
50 I2C_SDA
Control
I
2
C Data.
52
IN_D0
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
53
IP_D0
HS I
High Speed Input.
55
IN_D1
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
56
IP_D1
HS I
High Speed Input.
58
IN_D2
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
59
IP_D2
HS I
High Speed Input.
61
IN_D3
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
62
IP_D3
HS I
High Speed Input.
64
IN_C0
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
65
IP_C0
HS I
High Speed Input.
67
IN_C1
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
68
IP_C1
HS I
High Speed Input.
70
IN_C2
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
71
IP_C2
HS I
High Speed Input.
73
IN_C3
HS I
High Speed Input Complement.
74
IP_C3
HS I
High Speed Input.
76
PP_EN
Control
High Speed Output Enable Parallel Interface.
77
PP_EQ
Control
High Speed Equalization Selection Parallel Interface.
78
AUX_D3
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 32
Pin No.
Mnemonic
Type
1
Description
79
AUX_D2
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
80
AUX_D1
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
81
AUX_D0
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
82
AMUXVCC
Power
Positive Auxiliary Multiplexer Supply. 5V typical.
83
AUX_C3
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
84
AUX_C2
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
85
AUX_C1
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
86
AUX_C0
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
87
AUX_COM3
LS I/O
Low Speed Common Input/Output.
88
AUX_COM2
LS I/O
Low Speed Common Input/Output.
89
AUX_COM1
LS I/O
Low Speed Common Input/Output.
90
AUX_COM0
LS I/O
Low Speed Common Input/Output.
91
AUX_B3
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
92
AUX_B2
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
93
AUX_B1
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
94
AUX_B0
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
96
AUX_A3
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
97
AUX_A2
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
98
AUX_A1
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
99
AUX_A0
LS I/O
Low Speed Input/Output.
100
PP_OTO
Control
High Speed Output Termination Selection Parallel Interface.
1
HS = high speed, LS = low speed, I = input, O = output.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 32
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
T
A
= 27°C, AVCC = 3.3 V, VTTI = 3.3 V, VTTO = 3.3 V, DVCC = 3.3 V, AMUXVCC = 5 V, AVEE = 0 V, DVEE = 0 V, differential input
swing = 1000 mV, TMDS outputs terminated with external 50 resistors to 3.3 V, pattern = PRBS 2
7
- 1, data rate = 1.65 Gbps, unless
otherwise noted.
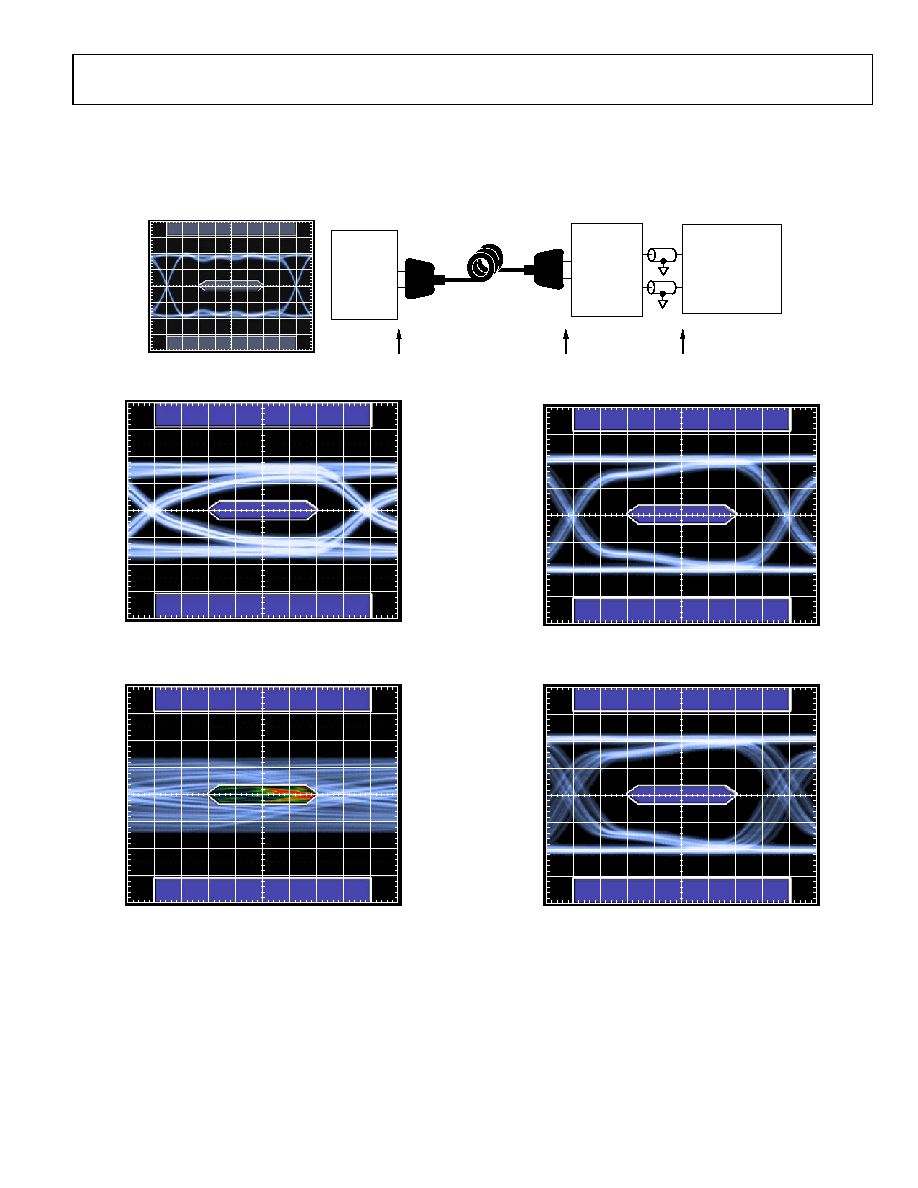
REFERENCE EYE DIAGRAM AT TP1
DIGITAL
PATTERN
GENERATOR
AD8191
EVALUATION
BOARD
SERIAL DATA
ANALYZER
SMA COAX CABLE
HDMI CABLE
TP1
TP2
TP3
0
612
3-
0
35
Figure 4. Test Circuit Diagram for RX Eye Diagram
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
36
Figure 5. RX Eye Diagram at TP2 (Cable = 2 meters, 30 AWG)
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
37
Figure 6. RX Eye Diagram at TP2 (Cable = 20 meters, 24 AWG)
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250m
V
/
DI
V
06
12
3-
0
38
Figure 7. RX Eye Diagram at TP3, EQ = 6 dB (Cable = 2 meters, 30 AWG)
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
39
Figure 8. RX Eye Diagram at TP3, EQ = 12 dB (Cable = 20 meters, 24 AWG)
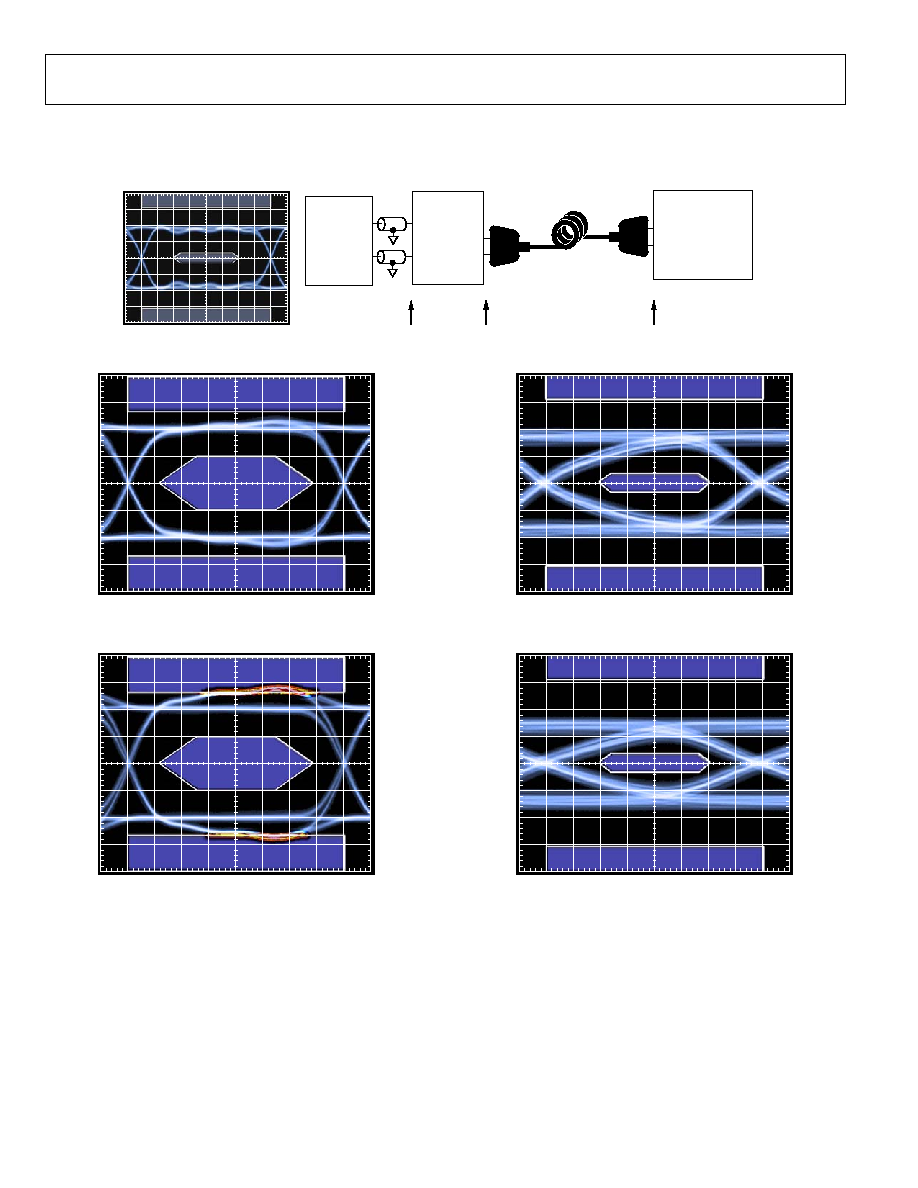
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 32
T
A
= 27°C, AVCC = 3.3 V, VTTI = 3.3 V, VTTO = 3.3 V, DVCC = 3.3 V, AMUXVCC = 5 V, AVEE = 0 V, DVEE = 0 V, differential input
swing = 1000 mV, TMDS outputs terminated with external 50 resistors to 3.3 V, pattern = PRBS 2
7
- 1, data rate = 1.65 Gbps, unless
otherwise noted.
REFERENCE EYE DIAGRAM AT TP1
DIGITAL
PATTERN
GENERATOR
SMA COAX CABLE
HDMI CABLE
TP1
TP2
TP3
AD8191
EVALUATION
BOARD
SERIAL DATA
ANALYZER
06
12
3-
0
40
Figure 9. Test Circuit Diagram for TX Eye Diagrams
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
41
Figure 10. TX Eye Diagram at TP2, PE = 2 dB
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
42
Figure 11. TX Eye Diagram at TP2, PE = 6 dB
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
43
Figure 12. TX Eye Diagram at TP3, PE = 2 dB (Cable = 2 meters, 30 AWG)
0.125UI/DIV AT 1.65Gbps
250
mV
/
D
I
V
06
12
3-
0
44
Figure 13. TX Diagram at TP3, PE = 6 dB (Cable = 10 meters, 28 AWG)
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 32
T
A
= 27°C, AVCC = 3.3 V, VTTI = 3.3 V, VTTO = 3.3 V, DVCC = 3.3 V, AMUXVCC = 5 V, AVEE = 0 V, DVEE = 0 V, differential input
swing = 1000 mV, TMDS outputs terminated with external 50 resistors to 3.3 V, pattern = PRBS 2
7
- 1, data rate = 1.65 Gbps, unless
otherwise noted.
0.5
0.6
0
0
35
0.6
0
0
25
HDMI CABLE LENGTH (m)
D
E
TE
R
M
IN
IS
TIC
J
I
TT
E
R
(
U
I)
HDMI CABLE LENGTH (m)
DE
T
E
RM
I
NI
S
T
I
C J
I
T
T
E
R (
U
I
)
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
5
10
15
20
25
30
2m CABLE = 30AWG
5m TO 10m CABLES = 28AWG
15m TO 30m CABLES = 24AWG
720p,
EQ = 12dB
1080p,
EQ = 12dB
480p,
EQ = 12dB
1.65Gbps,
EQ = 12dB
06
12
3-
01
4
DATA RATE (Gbps)
JI
T
T
E
R
(
p
s)
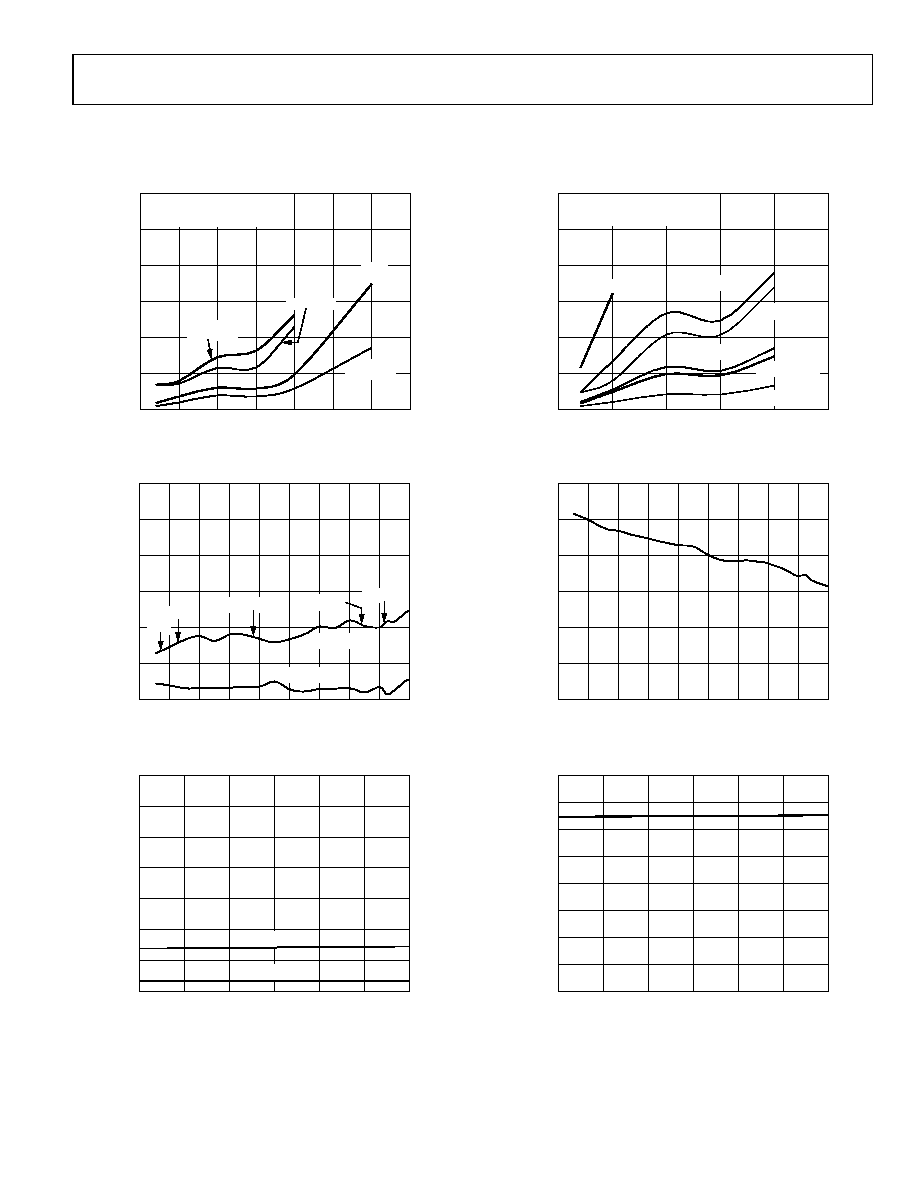
Figure 14. Jitter vs. Input Cable Length (See Figure 4 for Test Setup)
60
0
0
1.8
50
40
30
20
10
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
DJ (p-p)
RJ (rms)
06
12
3-
01
5
1.65Gbps
1080p
1080i/720p
480p
480i
Figure 15. Jitter vs. Data Rate
70
0
3.0
3.6
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
JI
T
T
E
R
(
p
s)
60
50
40
30
20
10
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
DJ (p-p)
RJ (rms)
06
12
3-
01
6
Figure 16. Jitter vs. Supply Voltage
2m CABLE = 30AWG
5m TO 10m CABLES = 28AWG
15m TO 20m CABLES = 24AWG
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
720p, PE OFF
5
10
15
20
1080p, MAX PE
720p, MAX PE
480p, PE OFF
480p, MAX PE
1080p, PE OFF
06
12
3-
01
7
1200
0
0
1.8
DATA RATE (Gbps)
E
Y
E
HE
I
G
HT
(
m
V
)
Figure 17. Jitter vs. Output Cable Length (See Figure 9 for Test Setup)
1000
800
600
400
200
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
06
12
3-
01
8
Figure 18. Eye Height vs. Data Rate
800
0
3.0
3.6
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
E
Y
E
HE
I
G
HT
(
m
V
)
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
06
12
3-
01
9
Figure 19. Eye Height vs. Supply Voltage
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 32
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT SWING (mV)
JI
T
T
E
R
(
p
s)
T
A
= 27°C, AVCC = 3.3 V, VTTI = 3.3 V, VTTO = 3.3 V, DVCC = 3.3 V, AMUXVCC = 5 V, AVEE = 0 V, DVEE = 0 V, differential input
swing = 1000 mV, TMDS outputs terminated with external 50 resistors to 3.3 V, pattern = PRBS 2
7
- 1, data rate = 1.65 Gbps, unless
otherwise noted.
30
0
0
2.0
50
0
2.5
INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
JI
T
T
E
R
(
p
s)
25
20
15
10
5
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
DJ (p-p)
RJ (rms)
DJ (p-p)
RJ (rms)
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
2.7
2.9
3.1
3.3
3.5
3.7
06
12
3-
02
3
06
12
3-
02
0
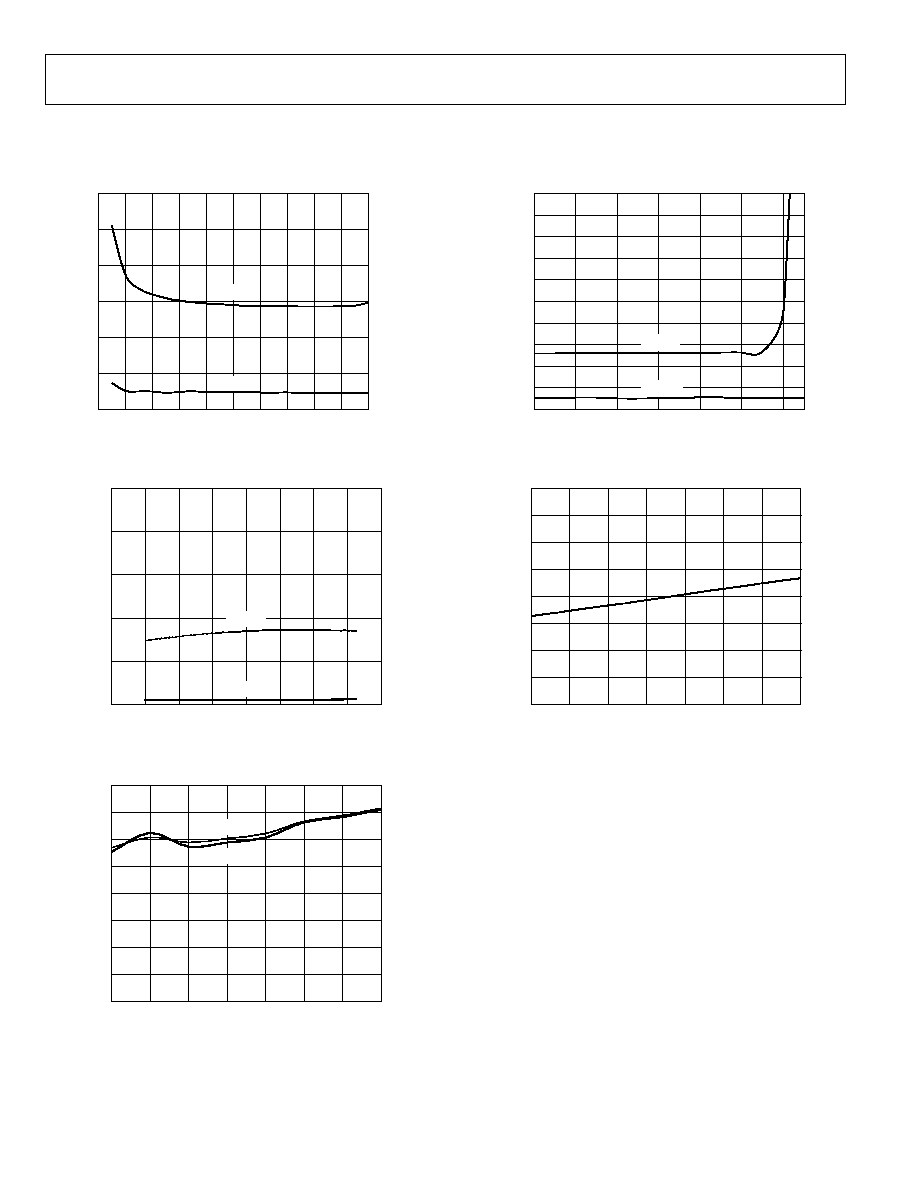
Figure 20. Jitter vs. Differential Input Swing
0
60
100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
JI
T
T
ER
(
p
s
)
40
20
0
20
40
60
80
40
50
30
20
10
RJ (rms)
DJ (p-p)
06
12
3-
02
1
Figure 21. Jitter vs. Temperature
160
0
40
100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
RI
S
E
/
F
AL
L
T
I
M
E
20% T
O
80
% (
p
s)
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
20
0
20
40
60
80
RISE TIME
FALL TIME
06
12
3-
02
2
Figure 22. Rise and Fall Time vs. Temperature
Figure 23. Jitter vs. Input Common-Mode Voltage
120
80
40
100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
D
I
FF
E
R
E
N
TI
A
L
I
N
P
U
T
T
E
R
M
I
NA
T
I
O
N RE
S
I
S
T
A
NCE
(
)
115
110
105
100
95
90
85
20
0
20
40
60
80
06
12
3-
02
4
Figure 24. Differential Input Termination Resistance vs. Temperature
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 32
THEORY OF OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
The primary function of the AD8191 is to switch one of four
(HDMI or DVI) single-link sources to one output. Each
HDMI/DVI link consists of four differential, high speed
channels and four auxiliary single-ended, low speed control
signals. The high speed channels include a data-word clock and
three transition minimized differential signaling (TMDS) data
channels running at 10× the data-word clock frequency for data
rates up to 1.65 Gbps. The four low speed control signals are
5 V tolerant bidirectional lines that can carry configuration
signals, HDCP encryption, and other information, depending
upon the specific application.
All four high speed TMDS channels in a given link are identical;
that is, the pixel clock can be run on any of the four TMDS
channels. Transmit and receive channel compensation is
provided for the high speed channels where the user can
(manually) select among a number of fixed settings.
The AD8191 switching logic has three modes: quad mode (a
quad 4:1 switch), dual mode (a dual 8:1 switch) and single
mode (one 16:1 switch).
The AD8191 has two control interfaces. Users have the option
of controlling the part through either the parallel control
interface or the I
2
C serial control interface. The AD8191 has
eight user-programmable I
2
C slave addresses to allow multiple
AD8191s to be controlled by a single I
2
C bus. A RESET pin is
provided to restore the control registers of the AD8191 to
default values. In all cases, serial programming values override
any prior parallel programming values and any use of the serial
control interface disables the parallel control interface until the
AD8191 is reset.
When using the serial control interface, all three switching
modes (quad, dual, and single) are accessible and the high speed
channel switching mode is controlled independently of the
auxiliary signal switching mode. When using the parallel
control interface, only the quad switching mode is accessible,
and the same channel select bus (PP_CH[1:0]) simultaneously
switches both the high speed channels and the auxiliary signals.
INPUT CHANNELS
Each high speed input differential pair terminates to the 3.3 V
VTTI power supply through a pair of single-ended 50 on-
chip resistors, as shown in Figure 25. The input terminations
can be optionally disconnected for approximately 100 ms
following a source switch. The user can program which of the
16 high speed input channels employs this feature by selectively
programming the associated RX_PT bits in the input
termination pulse register through the serial control interface.
Additionally, all the input terminations can be disconnected by
programming the RX_TO bit in the receiver settings register. By
default, the input termination is enabled. The input
terminations are enabled and cannot be switched when
programming the AD8191 through the parallel control
interface.
CABLE
EQ
50
50
IP_xx
IN_xx
AVEE
VTTI
0
6
123
-
00
4
Figure 25. High Speed Input Simplified Schematic
The input equalizer can be manually configured to provide two
different levels of high frequency boost: 6 dB or 12 dB. The user
can individually control the equalization level of the eight high
speed input channels by selectively programming the associated
RX_EQ bits in the receive equalizer register through the serial
control interface. Alternately, the user can globally control the
equalization level of all eight high speed input channels by
setting the PP_EQ pin of the parallel control interface. No
specific cable length is suggested for a particular equalization
setting because cable performance varies widely between
manufacturers; however, in general, the equalization of the
AD8191 can be set to 12 dB without degrading the signal
integrity, even for short input cables. At the 12 dB setting, the
AD8191 can equalize more than 20 meters of 24 AWG cable at
1.65 Gbps.
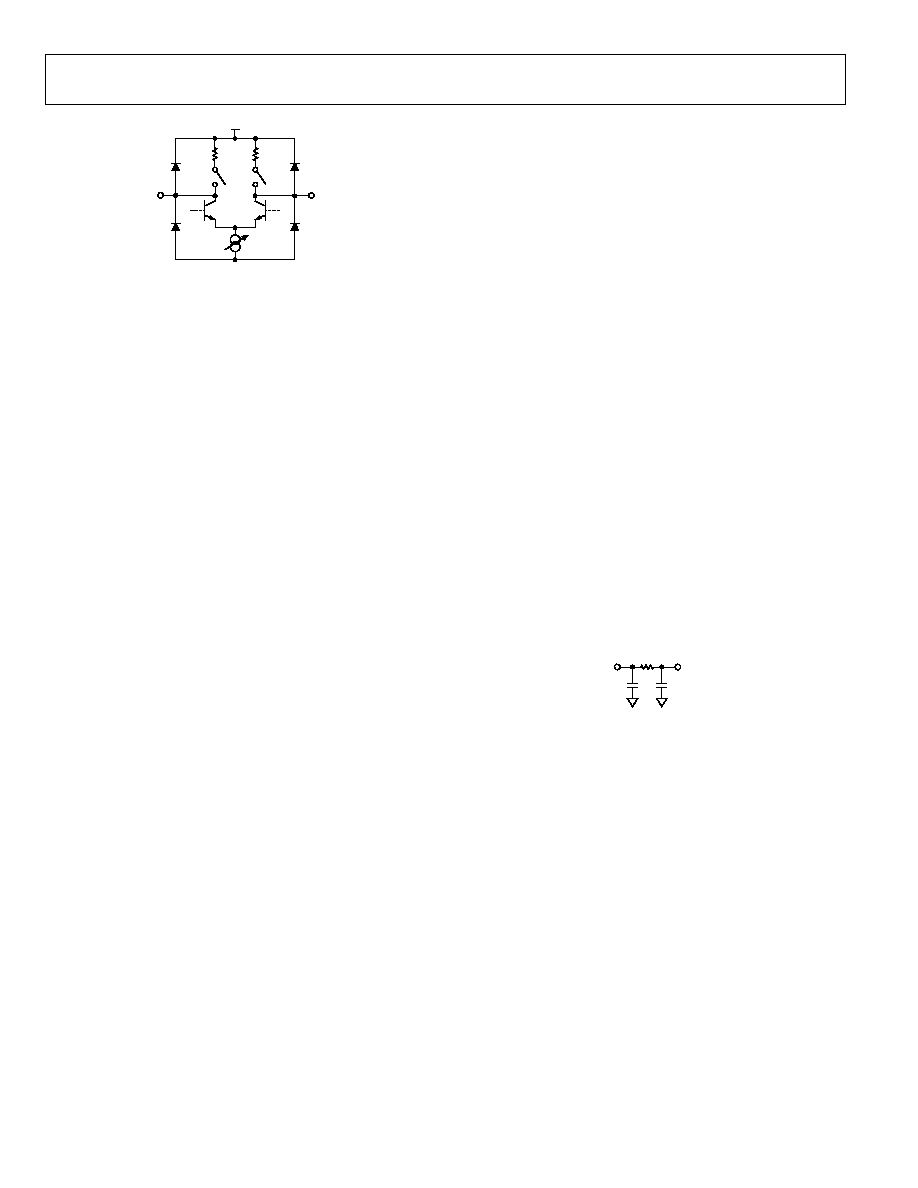
OUTPUT CHANNELS
Each high speed output differential pair is terminated to the
3.3 V VTTO power supply through a 50 on-chip resistor
(Figure 26). This termination is user-selectable; it can be turned
on or off by programming the TX_PTO bit of the transmitter
settings register through the serial control interface, or by
setting the PP_OTO pin of the parallel control interface.
The output termination resistors of the AD8191 back-terminate
the output TMDS transmission lines. These back-terminations
act to absorb reflections from impedance discontinuities on the
output traces, improving the signal integrity of the output traces
and adding flexibility to how the output traces can be routed.
For example, interlayer vias can be used to route the AD8191
TMDS outputs on multiple layers of the PCB without severely
degrading the quality of the output signal.
The AD8191 output has a disable feature that places the outputs
in a tristate mode. This mode is enabled by programming the
HS_EN bit of the high speed device modes register through the
serial control interface or by setting the PP_EN pin of the
parallel control interface. Larger wire-OR'ed arrays can be
constructed using the AD8191 in this mode.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 32
VTTO
50
50
OPx
ONx
AVEE
DISABLE
I
OUT
0
61
23
-
0
05
Figure 26. High Speed Output Simplified Schematic
The AD8191 requires output termination resistors when the
high speed outputs are enabled. Termination can be internal
and/or external. The internal terminations of the AD8191 are
enabled by programming the TX_PTO bit of the transmitter
settings register or by setting the PP_OTO pin of the parallel
control interface. The internal terminations of the AD8191
default to the setting indicated by PP_OTO upon reset. External
terminations can be provided either by on-board resistors or by
the input termination resistors of an HDMI/DVI receiver. If
both the internal terminations are enabled and external termi-
nations are present, set the output current level to 20 mA by
programming the TX_OCL bit of the transmitter settings
register through the serial control interface or by setting the
PP_OCL pin of the parallel control interface. The output
current level defaults to the level indicated by PP_OCL upon
reset. If only external terminations are provided (if the internal
terminations are disabled), set the output current level to 10 mA
by programming the TX_OCL bit of the transmitter settings
register or by setting the PP_OCL pin of the parallel control
interface. The high speed outputs must be disabled if there are
no output termination resistors present in the system.
The output pre-emphasis can be manually configured to provide
one of four different levels of high frequency boost. The specific
boost level is selected by programming the TX_PE bits of the
transmitter settings register through the serial control interface,
or by setting the PP_PE bus of the parallel control interface. No
specific cable length is suggested for a particular pre-emphasis
setting because cable performance varies widely between
manufacturers.
HIGH SPEED (TMDS) SWITCHING MODES
The AD8191 has three high speed switching modes: quad, dual,
and single. These are selected by programming the HS_SM bits
of the high speed device modes register through the serial
control interface.
Quad Switching Mode
This is the default mode. In quad mode, the AD8191 behaves
like a 4:1 HDMI/DVI link multiplexer routing groups of four
TMDS input channels to the four-channel output. This mode is
accessible through both the serial and the parallel control
interfaces. When using the serial control interface, the user
selects which TMDS link is routed to the output by
programming the HS_CH bits of the high speed device modes
register in accordance with the switch mapping listed in Table 8.
When using the parallel control interface, the user selects which
TMDS link is routed to the output by setting the PP_CH bus of
the parallel control interface in accordance with the switch
mapping listed in Table 26.
Dual Switching Mode
In this mode, the AD8191 behaves as a locked dual [8:1] TMDS
channel switch. The two 8:1 switches share the channel select
input and, therefore, switch together. The user selects which two
out of the eight possible input groups are routed to output by
programming the HS_CH bits of the high speed device modes
register in accordance with the switch mapping listed in Table 9.
This mode is only accessible through the serial control interface.
Single Switching Mode
In this mode, the AD8191 behaves as a single 16:1 TMDS
channel multiplexer; one of the 16 input channels is routed to
all of the outputs. The user selects which input channel is
routed to the outputs by programming the HS_CH bits in the
high speed device modes register in accordance with the switch
mapping listed in Table 10. This mode is only accessible
through the serial control interface.
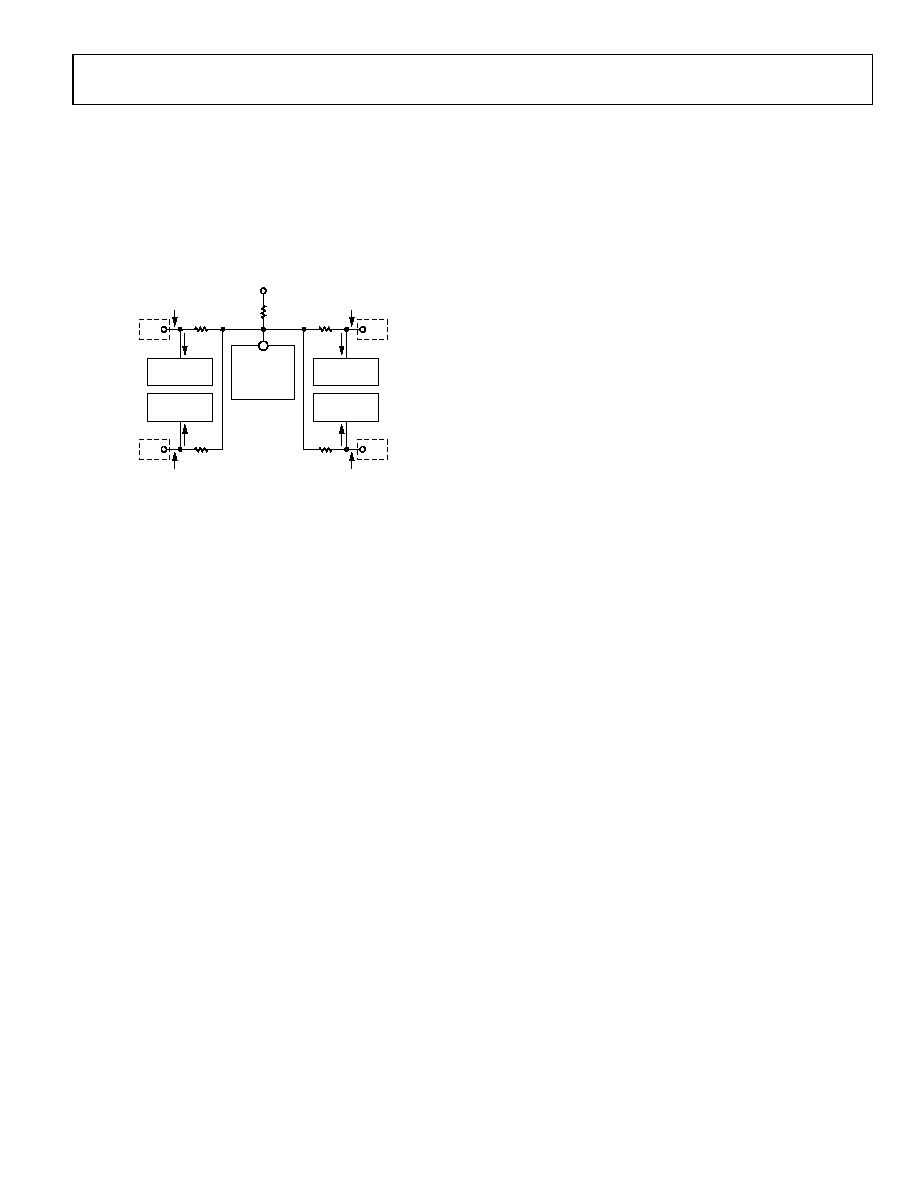
AUXILIARY SWITCH
The auxiliary (low speed) lines have no amplification. They are
routed using a passive switch that is bandwidth compatible with
standard speed I
2
C. The schematic equivalent for this passive
connection is shown in Figure 27.
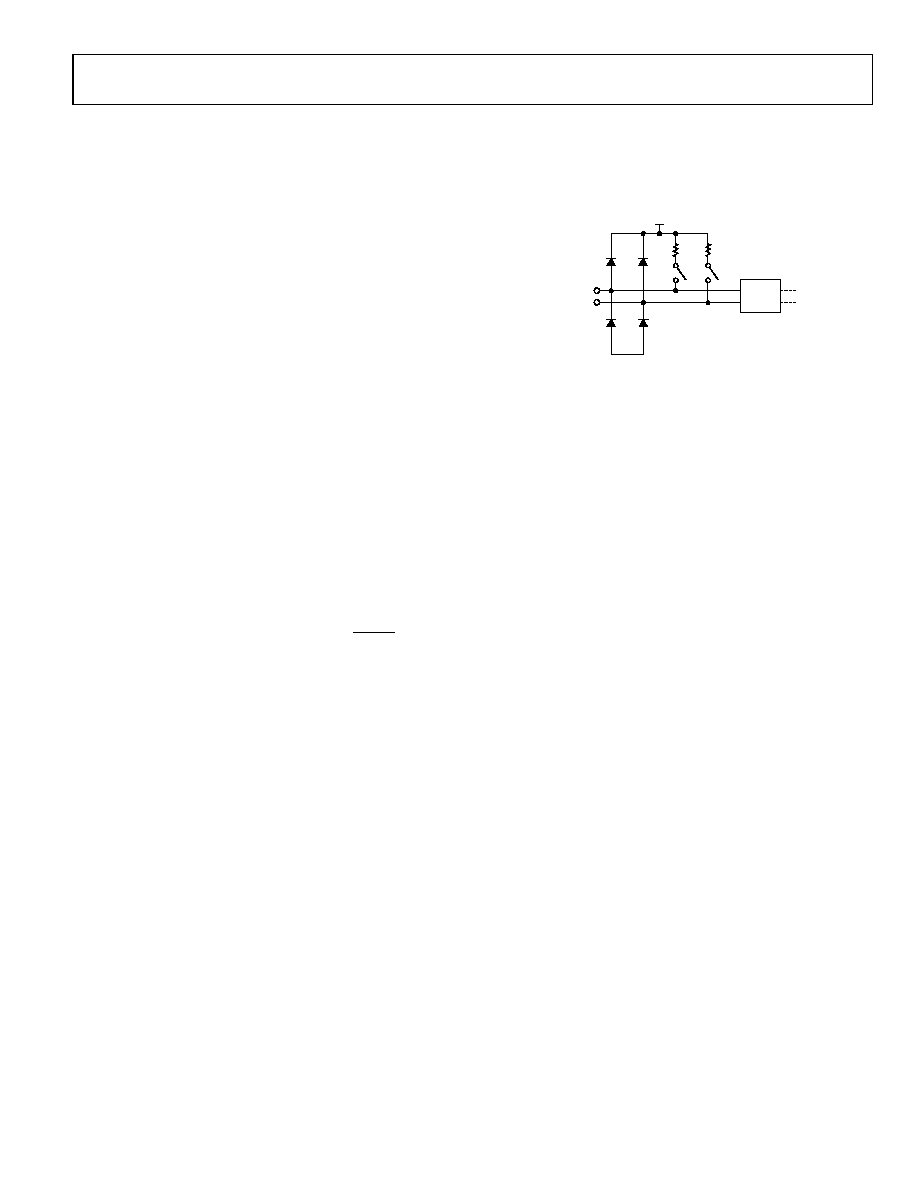
AUX_COM0
AUX_A0
½C
AUX
½C
AUX
R
AUX
06
12
3-
00
6
Figure 27. Auxiliary Channel Simplified Schematic,
AUX_A0 to AUX_COM0 Routing Example
When turning off the AD8191, care needs to be taken with
the AMUXVCC supply to ensure that the auxiliary multiplexer
pins remain in a high impedance state. A scenario that illustrates
this requirement is one where the auxiliary multiplexer is used
to switch the display data channel (DDC) bus. In some applica-
tions, additional devices can be connected to the DDC bus
(such as an EEPROM with EDID information) upstream of the
AD8191. Extended display identification data (EDID) is a VESA
standard-defined data format for conveying display configuration
information to sources to optimize display use. EDID devices
may need to be available via the DDC bus, regardless of the
state of the AD8191 and any downstream circuit. For this
configuration, the auxiliary inputs of the powered down
AD8191 need to be in a high impedance state to avoid pulling
down on the DDC lines and preventing these other devices
from using the bus.
When the AD8191 is powered from a simple resistor network,
as shown in Figure 28, it uses the 5 V supply that is required
from any HDMI/DVI source to guarantee high impedance of
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 32
the auxiliary multiplexer pins. The AMUXVCC supply does not
draw any static current; therefore, it is recommended that the
resistor network tap the 5 V supplies as close to the connectors
as possible to avoid any additional voltage drop.
This precaution does not need to be taken if the DDC
peripheral circuitry is connected to the bus downstream of
the AD8191.
PERIPHERAL
CIRCUITRY
PERIPHERAL
CIRCUITRY
+5V SOURCE C
+5V SOURCE D
PIN 18 HDMI CONNECTOR
PIN 14 DVI CONNECTOR
PIN 18 HDMI CONNECTOR
PIN 14 DVI CONNECTOR
10k
10M
10k
|<50mA
|<50mA
PERIPHERAL
CIRCUITRY
PERIPHERAL
CIRCUITRY
SOURCE A +5V
SOURCE B +5V
PIN 18 HDMI CONNECTOR
PIN 14 DVI CONNECTOR
PIN 18 HDMI CONNECTOR
PIN 14 DVI CONNECTOR
10k
10k
|<50mA
|<50mA
AMUXVCC
AD8191
+5V INTERNAL
(IF ANY)
0
61
23
-
00
7
Figure 28. Suggested AMUXVCC Power Scheme
AUXILIARY (LOW SPEED) SWITCHING MODES
The AD8191 has three auxiliary switching modes: quad, dual,
and single. These are selected by programming the AUX_SM
bits of the auxiliary device modes register through the serial
control interface. The auxiliary switching mode is independent
of the high speed switching mode whenever the part is
controlled through the serial control interface. When the part is
controlled through the parallel control interface, however, only
quad mode is accessible and the auxiliary switching mode
cannot be independently controlled.
Quad Switching Mode
This is the default mode. In quad mode, the AD8191 behaves
like a 4:1 auxiliary link multiplexer, routing groups of four
auxiliary input signals to the four-signal output. The user can
select which group of inputs is routed to the output by program-
ming the AUX_CH bits of the auxiliary device modes register
through the serial control interface in accordance with the
switch mapping listed in Table 13. Alternately, the user can
select which group of inputs is routed to the output by setting
the PP_CH bus of the parallel control interface in accordance
with the switch mapping listed in Table 27.
Dual Switching Mode
In this mode, the AD8191 behaves as a locked dual [8:1]
auxiliary signal switch. The two 8:1 switches share the channel
select input and, therefore, switch together. The user selects
which two out of the eight possible input groups are routed to
the output by programming the AUX_CH bits of the auxiliary
device modes register in accordance with the switch mapping
listed in Table 14. This mode is only accessible through the
serial control interface.
Single Switching Mode
In this mode the AD8191 behaves as a single 16:1 TMDS
channel multiplexer; a single channel, out of a possible 16, is
routed to all of the outputs. The user selects which input
channel is routed to the outputs by programming the AUX_CH
bits of the auxiliary device modes register in accordance with
the switch mapping listed in Table 15. This mode is only
accessible through the serial control interface.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 32
SERIAL CONTROL INTERFACE
RESET
On initial power-up, or at any point in operation, the AD8191
register set can be restored to preprogrammed default values by
pulling the RESET pin to low in accordance with the specifica-
tions in Table 1. During normal operation, however, the RESET
pin must be pulled up to 3.3 V. Following a reset, the prepro-
grammed default values of the AD8191 register set correspond
to the state of the parallel interface configuration registers, as
listed in Table 24. The AD8191 can be controlled through the
parallel control interface until the first serial control event
occurs. As soon as any serial control event occurs, the serial
programming values, corresponding to the state of the serial
interface configuration registers (Table 5), override any prior
parallel programming values, and the parallel control interface
is disabled until the part is subsequently reset.
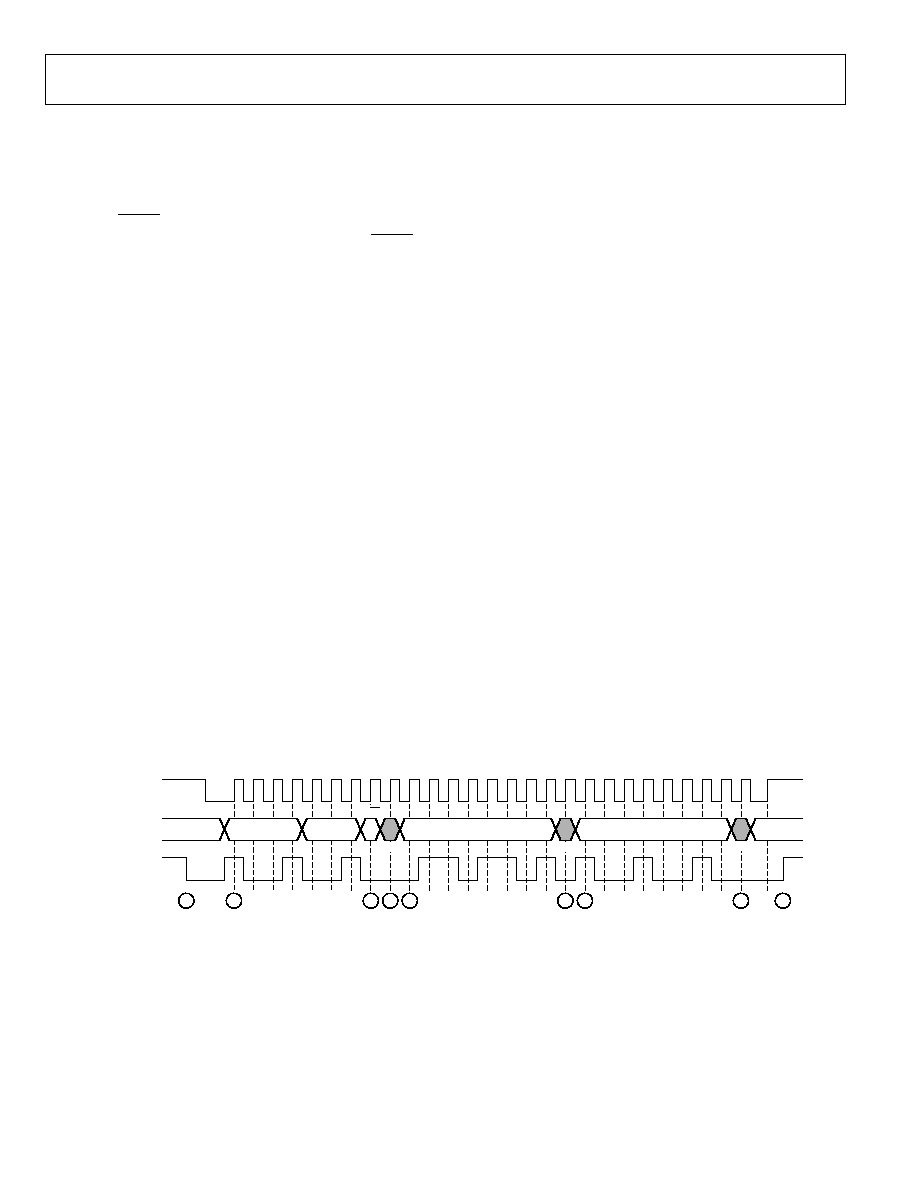
WRITE PROCEDURE
To write data to the AD8191 register set, an I
2
C master (such as
a microcontroller) needs to send the appropriate control signals
to the AD8191 slave device. The signals are controlled by the
I
2
C master, unless otherwise specified. For a diagram of the
procedure, see Figure 29. The steps for a write procedure are as
follows:
1.
Send a start condition (while holding the I2C_SCL line
high, pull the I2C_SDA line low).
2.
Send the AD8191 part address (seven bits). The upper four
bits of the AD8191 part address are the static value [1001]
and the three LSBs are set by Input Pin I2C_ADDR2, Input
Pin I2C_ADDR1, and Input Pin I2C_ADDR0 (LSB). This
transfer should be MSB first.
3.
Send the write indicator bit (0).
4.
Wait for the AD8191 to acknowledge the request.
5.
Send the register address (eight bits) to which data is to be
written. This transfer should be MSB first.
6.
Wait for the AD8191 to acknowledge the request.
7.
Send the data (eight bits) to be written to the register
whose address was set in Step 5. This transfer should be
MSB first.
8.
Wait for the AD8191 to acknowledge the request.
9.
Perform one of the following:
9a.
Send a stop condition (while holding the I2C_SCL
line high, pull the I2C_SDA line high) and release
control of the bus to end the transaction (shown in
Figure 29).
9b.
Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
I2C_SCL line high, pull the I2C_SDA line low) and
continue with Step 2 in this procedure to perform
another write.
9c.
Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
I2C_SCL line high, pull the I2C_SDA line low) and
continue with Step 2 of the read procedure (in the
Read Procedure section) to perform a read from
another address.
9d.
Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
I2C_SCL line high, pull the I2C_SDA line low) and
continue with Step 8 of the read procedure (in the
Read Procedure section) to perform a read from the
same address set in Step 5.
R/W
ACK
ACK
ADDR
START
FIXED PART
ADDR
REGISTER ADDR
DATA
STOP
ACK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
I2C_SCL
GENERAL CASE
I2C_SDA
EXAMPLE
I2C_SDA
*THE SWITCHING/UPDATE DELAY BEGINS AT THE FALLING EDGE OF THE
LAST DATA BIT; FOR EXAMPLE, THE FALLING EDGE JUST BEFORE STEP 8.
*
06
12
3-
00
8
Figure 29. I
2
C Write Diagram
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 32
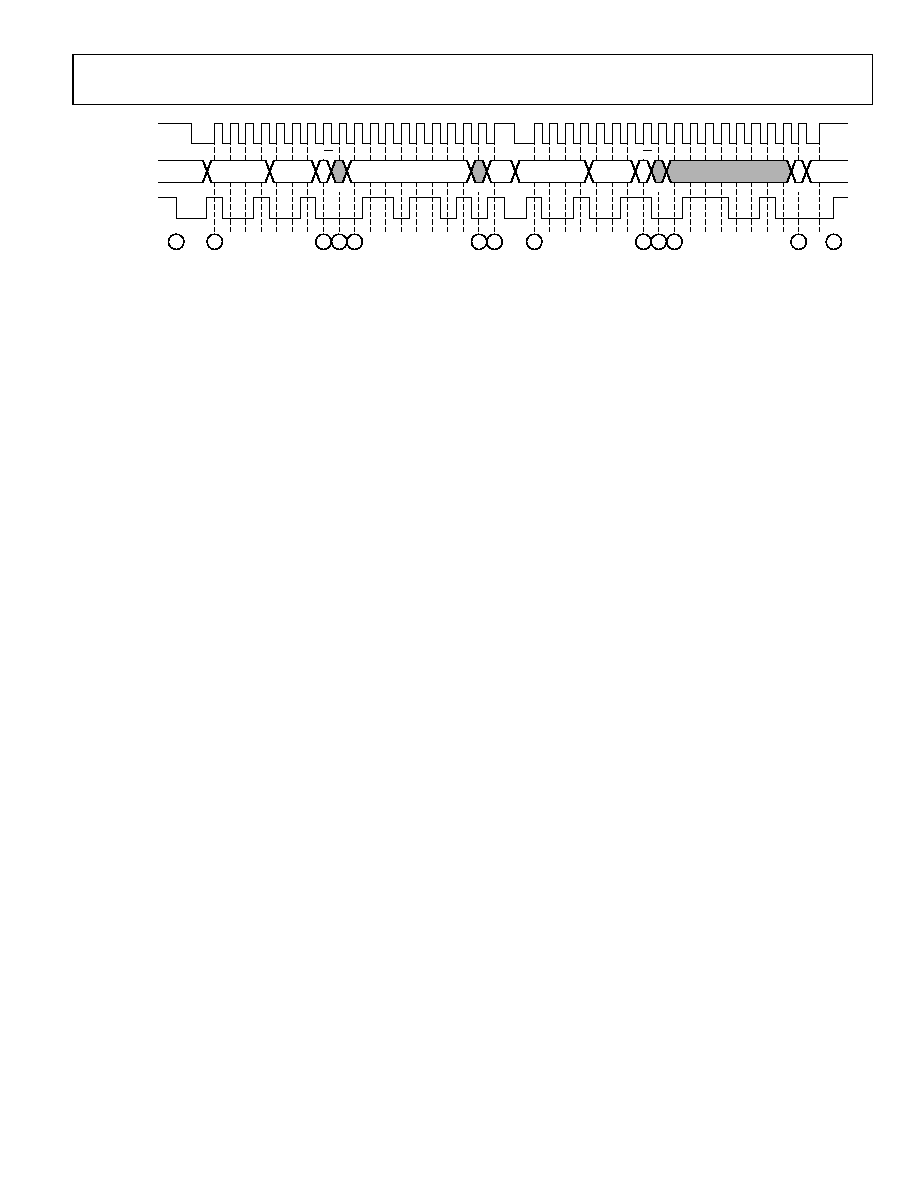
START
FIXED PART
ADDR
REGISTER ADDR
FIXED PART
ADDR
DATA
STOP
ACK
ADDR
ACK
R/W
ADDR
ACK
ACK
R/W
SR
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11
12
13
I2C_SCL
GENERAL CASE
I2C_SDA
EXAMPLE
I2C_SDA
06
12
3-
0
09
Figure 30. I
2
C Read Diagram
READ PROCEDURE
To read data from the AD8191 register set, an I
2
C master (such
as a microcontroller) needs to send the appropriate control
signals to the AD8191 slave device. The signals are controlled
by the I
2
C master, unless otherwise specified. For a diagram of
the procedure, see Figure 30. The steps for a read procedure are
as follows:
1.
Send a start condition (while holding the I2C_SCL line
high, pull the I2C_SDA line low).
2.
Send the AD8191 part address (seven bits). The upper four
bits of the AD8191 part address are the static value [1001]
and the three LSBs are set by Input Pin I2C_ADDR2, Input
Pin I2C_ADDR1, and Input Pin I2C_ADDR0 (LSB). This
transfer should be MSB first.
3.
Send the write indicator bit (0).
4.
Wait for the AD8191 to acknowledge the request.
5.
Send the register address (eight bits) from which data is to
be read. This transfer should be MSB first.
6.
Wait for the AD8191 to acknowledge the request.
7.
Send a repeated start condition (Sr) by holding the
I2C_SCL line high and pulling the I2C_SDA line low.
8.
Resend the AD8191 part address (seven bits) from Step 2.
The upper four bits of the AD8191 part address are the
static value [1001] and the three LSBs are set by the Input
Pin I2C_ADDR2, I2C_ADDR1 and Input Pin I2C_ADDR0
(LSB). This transfer should be MSB first.
9.
Send the read indicator bit (1).
10.
Wait for the AD8191 to acknowledge the request.
11.
The AD8191 serially transfers the data (eight bits) held in
the register indicated by the address set in Step 5. This data
is sent MSB first.
12.
Acknowledge the data from the AD8191.
13.
Perform one of the following:
13a.
S
op condition (while holding the I2C_SCL
line high, pull the SDA line high) and release control
of the bus to end the transaction (shown in
end a st
).
13b.
ated start condition (while holding the
13c.
13d.
on (while holding the
Figure 30
Send a repe
I2C_SCL line high, pull the I2C_SDA line low) and
continue with Step 2 of the write procedure (previous
Write Procedure section) to perform a write.
Send a repeated start condition (while holding the
I2C_SCL line high, pull the I2C_SDA line low) and
continue with Step 2 of this procedure to perform a
read from another address.
Send a repeated start conditi
I2C_SCL line high, pull the I2C_SDA line low) and
continue with Step 8 of this procedure to perform a
read from the same address.

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 32
PARALLEL CONTROL INTERFACE
The AD8191 can be controlled through the parallel interface
using the PP_EN, PP_CH[1:0], PP_EQ, PP_PRE[1:0], PP_OTO,
and PP_OCL pins. Logic levels for the parallel interface pins
are set in accordance with the specifications listed in Table 1.
Setting these pins updates the parallel control interface
registers, as listed in Table 24. Following a reset, the AD8191
can be controlled through the parallel control interface until the
first serial control event occurs. As soon as any serial control
event occurs, the serial programming values override any prior
parallel programming values, and the parallel control interface
is disabled until the part is subsequently reset. The default serial
programming values correspond to the state of the serial
interface configuration registers, as listed in Table 5.
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 32
SERIAL INTERFACE CONFIGURATION REGISTERS
The serial interface configuration registers can be read and written using the I
2
C serial control interface, Pin I2C_SDA, and Pin I2C_SCL.
The least significant bits of the AD8191 I
2
C part address are set by tying the Pin I2C_ADDR2, Pin I2C_ADDR1, and Pin I2C_ADDR0 to
3.3 V (Logic 1) or 0 V (Logic 0). As soon as the serial control interface is used, the parallel control interface is disabled until the AD8191
is reset as described in the Serial Control Interface section.
Table 5. Serial (I
2
C) Interface Register Map
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Addr.
Default
High
speed
switch
enable
High speed switching
mode select
High speed source select
High Speed
Device
Modes
HS_EN HS_SM[1] HS_SM[0] HS_CH[3] HS_CH[2] HS_CH[1] HS_CH[0]
0x00 0x40
Auxiliary
switch
enable
Auxiliary switching
mode select
Auxiliary switch source select
Auxiliary
Device
Modes
AUX_EN AUX_SM[1] AUX_SM[0] AUX_CH[3] AUX_CH[2] AUX_CH[1] AUX_CH[0]
0x01 0x40
High speed
input
termination
select
Receiver
Settings
RX_TO
0x10 0x01
Source A and Source B : input termination pulse-on-source switch select
(disconnect termination for a short period of time)
Input
Termination
Pulse 1
RX_PT[7]
RX_PT[6]
RX_PT[5] RX_PT[4] RX_PT[3] RX_PT[2] RX_PT[1] RX_PT
[0]
0x11 0x00
Source C and Source D: input termination pulse-on-source switch select
(disconnect termination for a short period of time)
Input
Termination
Pulse 2
RX_PT[15] RX_PT[14] RX_PT[13] RX_PT[12] RX_PT[11] RX_PT[10] RX_PT[9]
RX_PT[8]
0x12 0x00
Source A and Source B: input equalization level select
Receive
Equalizer 1
RX_EQ[7] RX_EQ[6] RX_EQ[5] RX_EQ[4] RX_EQ[3] RX_EQ[2] RX_EQ[1] RX_EQ[0]
0x13 0x00
Source C and Source D: input equalization level select
Receive
Equalizer 2
RX_EQ[15] RX_EQ[14] RX_EQ[13] RX_EQ[12] RX_EQ[11] RX_EQ[10] RX_EQ[9]
RX_EQ[8]
0x14 0x00
High speed output
pre-emphasis level select
High speed
output
termination
select
High speed
output
current level
select
Transmitter
Settings
TX_PE[1] TX_PE[0] TX_PTO
TX_OCL
0x20 0x03
HIGH SPEED DEVICE MODES REGISTER
HS_EN: High Speed (TMDS) Channels Enable Bit
Table 6. HS_EN Description
HS_EN Description
0
High speed channels off, low power/standby mode
1
High speed channels on
HS_SM[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Switching Mode
Select Bus
Table 7. HS_SM Description
HS_SM[1:0] Description
00
Quad mode, 4× [4:1]
01
Dual mode, 2× [8:1]
10
Single mode, 1× [16:1]
11
Illegal value; previous value of HS_SM[1:0]
retained
HS_CH[3:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Switch Source Select Bus
Table 8. Quad Mode, 4× [4:1], High Speed Switch Mapping
HS_CH[3:0] O[3:0] Description
XX00 A[3:0]
High Speed Source A switched to
output
XX01 B[3:0]
High Speed Source B switched to
output
XX10 C[3:0]
High Speed Source C switched to
output
XX11 D[3:0]
High Speed Source D switched to
output
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 32
Table 9. Dual Mode, 2× [8:1], High Speed Switch Mapping
HS_CH[3:0] O[3:2] O[1:0] Description
X000 A1
A0
The A0 and A1 high speed
channels switched to output
X001 A3
A2
The A2 and A3 high speed
channels switched to output
X010 B1
B0
The B0 and B1 high speed
channels switched to output
X011 B3
B2
The B2 and B3 high speed
channels switched to output
X100 C1
C0
The C0 and C1 high speed
channels switched to output
X101 C3
C2
The C2 and C3 high speed
channels switched to output
X110 D1
D0
The D0 and D1 high speed
channels switched to output
X111 D3
D2
The D2 and D3 high speed
channels switched to output
Table 10. Single Mode, 1× [16:1], High Speed Switch
Mapping
HS_CH[3:0] O[3:0] Description
0000 A0
High Speed Channel A0 switched to
output
0001 A1
High Speed Channel A1 switched to
output
0010 A2
High Speed Channel A2 switched to
output
0011 A3
High Speed Channel A3 switched to
output
0100 B0
High Speed Channel B0 switched to
output
0101 B1
High Speed Channel B1 switched to
output
0110 B2
High Speed Channel B2 switched to
output
0111 B3
High Speed Channel B3 switched to
output
1000 C0
High Speed Channel C0 switched to
output
1001 C1
High Speed Channel C1 switched to
output
1010 C2
High Speed Channel C2 switched to
output
1011 C3
High Speed Channel C3 switched to
output
1100 D0
High Speed Channel D0 switched to
output
1101 D1
High Speed Channel D1 switched to
output
1110 D2
High Speed Channel D2 switched to
output
1111 D3
High Speed Channel D3 switched to
output
AUXILIARY DEVICE MODES REGISTER
AUX_EN: Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switch Enable Bit
Table 11. AUX_EN Description
AUX_EN Description
0
Auxiliary switch off, no low speed input/output
to low speed common input/output
connection
1 Auxiliary
switch
on
AUX_SM[1:0]: Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switching Mode
Select Bus
Table 12. AUX_SM[1:0] Description
AUX_SM[1:0] Description
00
Quad Mode, 4× [4:1]
01
Dual Mode, 2× [8:1]
10
Single Mode, 1× [6:1]
11
Illegal value; previous value of AUX_SM[1:0]
retained
AUX_CH[3:0]: Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switch Source
Select Bus
Table 13. Quad Mode, 4× [4:1], Auxiliary Switch Mapping
AUX_CH[3:0] AUX_COM[3:0] Description
XX00 AUX_A[3:0]
Auxiliary Source A switched
to output
XX01 AUX_B[3:0]
Auxiliary Source B switched
to output
XX10 AUX_C[3:0]
Auxiliary Source C switched
to output
XX11 AUX_D[3:0]
Auxiliary Source D switched
to output
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 32
Table 14. Dual Mode, 2× [8:1], Auxiliary Switch Mapping
AUX_CH[3:0] AUX_COM[3:2] AUX_COM[1:0] Description
X000 AUX_C0 AUX_A0
The A0 and
C0 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X001 AUX_C1 AUX_A1
The A1 and
C1 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X010 AUX_C2 AUX_A2
The A2 and
C2 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X011 AUX_C3 AUX_A3
The A3 and
C3 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X100 AUX_D0
AUX_B0 The B0 and
D0 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X101 AUX_D1
AUX_B1 The B1 and
D1 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X110 AUX_D2
AUX_B2 The B2 and
D2 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
X111 AUX_D3
AUX_B3 The B3 and
D3 auxiliary
channels
switched to
output
Table 15. Single Mode, 1× [16:1], Auxiliary Switch Mapping
AUX_CH[3:0] AUX_COM[3:0] Description
0000 AUX_A0
Auxiliary Channel A0
switched to output
0001 AUX_A1
Auxiliary Channel A1
switched to output
0010 AUX_A2
Auxiliary Channel A2
switched to output
0011 AUX_A3
Auxiliary Channel A3
switched to output
0100 AUX_B0 Auxiliary Channel B0
switched to output
0101 AUX_B1 Auxiliary Channel B1
switched to output
0110 AUX_B2 Auxiliary Channel B2
switched to output
0111 AUX_B3 Auxiliary Channel B3
switched to output
1000 AUX_C0
Auxiliary Channel C0
switched to output
1001 AUX_C1
Auxiliary Channel C1
switched to output
1010 AUX_C2
Auxiliary Channel C2
switched to output
1011 AUX_C3
Auxiliary Channel C3
switched to output
1100 AUX_D0
Auxiliary Channel D0
switched to output
1101 AUX_D1
Auxiliary Channel D1
switched to output
1110 AUX_D2
Auxiliary Channel D2
switched to output
1111 AUX_D3
Auxiliary Channel D3
switched to output
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 32
RECEIVER SETTINGS REGISTER
RX_TO: High Speed (TMDS) Channels Input Termination
On/Off Select Bit
Table 16. RX_TO Description
RX_TO Description
0
Input termination off
1
Input termination on (can be pulsed on and off
according to settings in the input termination
pulse register)
INPUT TERMINATION PULSE REGISTER 1 AND
REGISTER 2
RX_PT[X]: High Speed (TMDS) Input Channel X
Pulse-On-Source Switch Select Bit
Table 17. RX_PT[X] Description
RX_PT[X] Description
0
Input termination for TMDS Channel X always
connected when source is switched
1
Input termination for TMDS Channel X
disconnected for 100 ms when source switched
Table 18. RX_PT[X] Mapping
RX_PT[X]
Corresponding Input TMDS Channel
Bit 0
B0
Bit 1
B1
Bit 2
B2
Bit 3
B3
Bit 4
A0
Bit 5
A1
Bit 6
A2
Bit 7
A3
Bit 8
C3
Bit 9
C2
Bit 10
C1
Bit 11
C0
Bit 12
D3
Bit 13
D2
Bit 14
D1
Bit 15
D0
RECEIVE EQUALIZER REGISTER 1 AND REGISTER 2
RX_EQ[X]: High Speed (TMDS) Input X Equalization Level
Select Bit
Table 19. RX_EQ[X] Description
RX_EQ[X] Description
0
Low equalization (6 dB)
1
High equalization (12 dB)
Table 20. RX_EQ[X] Mapping
RX_EQ[X]
Corresponding Input TMDS Channel
Bit 0
B0
Bit 1
B1
Bit 2
B2
Bit 3
B3
Bit 4
A0
Bit 5
A1
Bit 6
A2
Bit 7
A3
Bit 8
C3
Bit 9
C2
Bit 10
C1
Bit 11
C0
Bit 12
D3
Bit 13
D2
Bit 14
D1
Bit 15
D0
TRANSMITTER SETTINGS REGISTER
TX_PE[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Output Pre-Emphasis
Level Select Bus (For All TMDS Channels)
Table 21. TX_PE[1:0] Description
TX_PE[1:0] Description
00
No pre-emphasis (0 dB)
01
Low pre-emphasis (2 dB)
10
Medium pre-emphasis (4 dB)
11
High pre-emphasis (6 dB)
TX_PTO: High Speed (TMDS) Output Termination On/Off
Select Bit (For All Channels)
Table 22. TX_PTO Description
TX_PTO Description
0
Output termination off
1
Output termination on
TX_OCL:High Speed (TMDS) Output Current Level Select
Bit (For All Channels)
Table 23. TX_OCL Description
TX_OCL Description
0
Output current set to 10 mA
1
Output current set to 20 mA
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 32
PARALLEL INTERFACE CONFIGURATION REGISTERS
The parallel interface configuration registers can be directly set using the PP_EN, PP_CH[1:0], PP_EQ, PP_PRE[1:0], PP_OTO, and
PP_OCL pins. This interface is only accessible after the part is reset and before any registers are accessed using the serial control interface.
The state of each pin is set by tying it to 3.3 V (Logic 1) or 0 V (Logic 0).
Table 24. Parallel Interface Register Map
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
High speed
switch enable
High speed switching
mode select (quad)
High speed source select
High Speed
Device Modes
PP_EN 0 0 0 0 PP_CH[1] PP_CH[0]
Auxiliary
switch enable
Auxiliary switching
mode select (quad)
Auxiliary switch source select
Auxiliary Device
Modes
1
0 0 0 0 PP_CH[1] PP_CH[0]
Input term. on/off
select (termination
always on)
Receiver
Settings
1
Source A and Source B input termination pulse-on-source switch select (termination always on)
Input
Termination
Pulse 1
0
0
0 0 0 0 0
0
Source C and Source D input termination pulse-on-source switch select (termination always on)
Input
Termination
Pulse 2
0
0
0 0 0 0 0
0
Source A and Source B input equalization level select
Receive
Equalizer 1
PP_EQ PP_EQ
PP_EQ
PP_EQ
PP_EQ PP_EQ PP_EQ
PP_EQ
Source C and Source D input equalization level select
Receive
Equalizer 2
PP_EQ PP_EQ
PP_EQ
PP_EQ
PP_EQ PP_EQ PP_EQ
PP_EQ
Output pre-emphasis
level select
Output
termination
on/off select
Output current level
select
Transmitter
Settings
PP_PE[1] PP_PE[0] PP_OTO
PP_OCL
HIGH SPEED DEVICE MODES REGISTER
The high speed (TMDS) switching mode is fixed to quad mode
when using the parallel interface.
PP_EN: High Speed (TMDS) Channels Enable Bit
Table 25. PP_EN Description
PP_EN Description
0
High speed channels off, low power/standby mode
1
High speed channels on
PP_CH[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Switch Source Select Bus
Table 26. Quad High speed Switch Mode Mapping
PP_CH[1:0] O[3:0] Description
00 A[3:0]
High Speed Source A switched to
output
01 B[3:0]
High Speed Source B switched to
output
10 C[3:0]
High Speed Source C switched to
output
11 D[3:0]
High Speed Source D switched to
output
AUXILIARY DEVICE MODES REGISTER
The auxiliary (low speed) switch is always enabled and the
auxiliary switching mode is fixed to quad mode when using the
parallel interface.
PP_CH[1:0]: Auxiliary Switch Source Select Bus
Table 27. Quad Auxiliary Switch Mode Mapping
PP_CH[1:0] AUX_COM[3:0] Description
00 AUX_A[3:0]
Auxiliary Source A switched to
output
01 AUX_B[3:0]0
Auxiliary Source B switched to
output
10 AUX_C[3:0]
Auxiliary Source C switched to
output
11 AUX_D[3:0]
Auxiliary Source D switched to
output
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 32
RECEIVER SETTINGS REGISTER
High speed (TMDS) channels input termination is fixed to on
when using the parallel interface.
INPUT TERMINATION PULSE REGISTER 1 AND
REGISTER 2
High speed input (TMDS) channels pulse-on-source switching
fixed to off when using the parallel interface.
RECEIVE EQUALIZER REGISTER 1 AND REGISTER 2
PP_EQ: High Speed (TMDS) Inputs Equalization Level
Select Bit (For All TMDS Input Channels)
The input equalization cannot be set individually (per channel)
when using the parallel interface; one equalization setting
affects all input channels.
Table 28. PP_EQ Description
PP_EQ Description
0
Low equalization (6 dB)
1
High equalization (12 dB)
TRANSMITTER SETTINGS REGISTER
PP_PE[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Output Pre-Emphasis
Level Select Bus (For All TMDS Channels)
Table 29. PP_PE[1:0] Description
PP_PE[1:0] Description
00
No pre-emphasis (0 dB)
01
Low pre-emphasis (2 dB)
10
Medium pre-emphasis (4 dB)
11
High pre-emphasis (6 dB)
PP_OTO: High Speed (TMDS) Output Termination On/Off
Select Bit (For All TMDS Channels)
Table 30. PP_OTO Description
PP_OTO Description
0
Output termination off
1
Output termination on
PP_OCL: High Speed (TMDS) Output Current Level Select
Bit (For All TMDS Channels)
Table 31. TX_OCL Description
PP_OCL Description
0
Output current set to 10 mA
1
Output current set to 20 mA
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 32
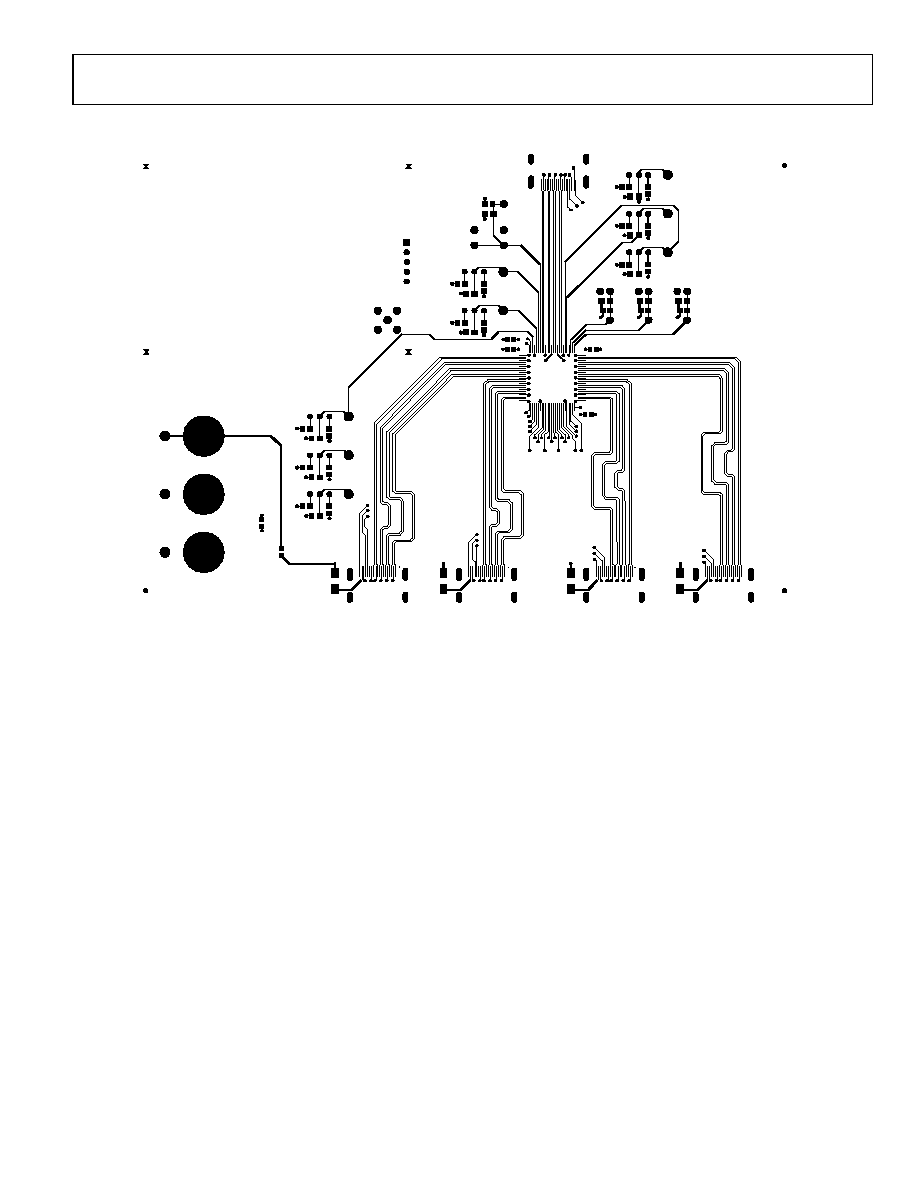
APPLICATION INFORMATION
0
61
23
-
0
31
Figure 31. Layout of the TMDS Traces on the AD8191 Evaluation Board (Only Top Signal Routing Layer is Shown)
The AD8191 is an HDMI/DVI switch featuring equalized
TMDS inputs and pre-emphasized TMDS outputs. It is in-
tended for use as a 4:1 switch in systems with long cable runs
on both the input and/or the output, and is fully HDMI 1.2a
receive-compliant.
PINOUT
The AD8191 is designed for an HDMI/DVI receiver pinout
at its input and a transmitter pinout at its output. This makes
the AD8191 ideal for use in AVR-type applications where the
designer routes both the inputs and the outputs directly to
HDMI/DVI connectors. This type of layout is used on the
AD8191 evaluation board, as shown in Figure 31. When the
AD8191 is used in receiver type applications, it is necessary to
change the ordering of the output pins on the PCB to match up
with the on-board receiver.
One advantage of the AD8191 in an AVR-type application is
that all of the high speed signals can be routed on one side (the
topside) of the board, as shown in Figure 31. In addition to
12 dB of input equalization, the AD8191 provides up to 6 dB of
output pre-emphasis that boosts the output TMDS signals and
allows the AD8191 to precompensate when driving long PCB
traces or output cables. The net effect of the input equalization
and output pre-emphasis of the AD8191 is that the AD8191 can
compensate for the signal degradation of both input and output
cables; it acts to reopen a closed input data eye and transmit a
full-swing HDMI signal to an end receiver.
The AD8191 also provides a distinct advantage in receive-type
applications because it is a fully buffered HDMI/DVI switch.
Although inverting the output pin order of the AD8191 on the
PCB requires a designer to place vias in the high speed signal
path, the AD8191 fully buffers and electrically decouples the
outputs from the inputs. Consequently, the effects of the vias
placed on the output signal lines are not seen at the input of the
AD8191. The programmable output terminations also improve
signal quality at the output of the AD8191. Therefore, the PCB
designer has significantly improved flexibility in the placement
and routing of the output signal path with the AD8191 over
other solutions.
CABLE LENGTHS AND EQUALIZATION
The AD8191 offers two levels of programmable equalization
for the high speed inputs: 6 dB and 12 dB. The equalizer of
the AD8191 is optimized for video data rates of 1.65 Gbps. It
can equalize up to 20 meters of 24 AWG HDMI cable at data rates
corresponding to the video format, 1080p.

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 32
The length of cable that can be used in a typical HDMI/DVI
application depends on a large number of factors, including:
·
Cable quality: the quality of the cable in terms of conductor
wire gauge and shielding. Thicker conductors have lower
signal degradation per unit length.
·
Data rate: the data rate being sent over the cable. The signal
degradation of HDMI cables increases with data rate.
·
Edge rates: the edge rates of the source input. Slower input
edges result in more significant data eye closure at the end
of a cable.
·
Receiver sensitivity: the sensitivity of the terminating
receiver.
As such, specific cable types and lengths are not recommended
for use with a particular equalizer setting. In nearly all applica-
tions, the AD8191 equalization level can be set to high, or 12 dB,
for all input cable configurations at all data rates, without
degrading the signal integrity.
PCB LAYOUT GUIDELINES
The AD8191 is used to switch two distinctly different types of
signals, both of which are required for HDMI and DVI video.
These signal groups require different treatment when laying out
a PC board.
The first group of signals carries the audiovisual (AV) data.
HDMI/DVI video signals are differential, unidirectional, and
high speed (up to 1.65 Gbps). The channels that carry the video
data must be controlled impedance, terminated at the receiver,
and capable of operating up to at least 1.65 Gbps. It is especially
important to note that the differential traces that carry the
TMDS signals should be designed with a controlled differential
impedance of 100 . The AD8191 provides single-ended, 50
terminations on-chip for both its inputs and outputs, and both
the input and output terminations can be enabled or disabled
through the serial interface. Transmitter termination is not fully
specified by the HDMI standard but its inclusion improves the
overall system signal integrity.
The audiovisual data carried on these high speed channels are
encoded by a technique called transmission minimized differ-
ential signaling (TMDS) and in the case of HDMI, is also encrypted
according to the high bandwidth digital copy protection (HDCP)
standard.
The second group of signals consists of low speed auxiliary
control signals used for communication between a source and a
sink. Depending upon the application, these signals can include
the DDC bus (this is an I
2
C bus used to send EDID information
and HDCP encryption keys between the source and the sink),
the consumer electronics control (CEC) line, and the hot plug
detect (HPD) line. These auxiliary signals are bidirectional, low
speed, and transferred over a single-ended transmission line
that does not need to have controlled impedance. The primary
concern with laying out the auxiliary lines is ensuring that they
conform to the I
2
C bus standard and do not have excessive
capacitive loading.
TMDS Signals
In the HDMI/DVI standard, four differential pairs carry the
TMDS signals. In DVI, three of these pairs are dedicated to
carrying RGB video and sync data. For HDMI, audio data is
interleaved with the video data; the DVI standard does not
incorporate audio information. The fourth high speed differ-
ential pair is used for the AV data-word clock, and runs at
one-tenth the speed of the TMDS data channels.
The four high speed channels of the AD8191 are identical.
No concession was made to lower the bandwidth of the fourth
channel for the pixel clock, so any channel can be used for any
TMDS signal. The user chooses which signal is routed over
which channel. Additionally, the TMDS channels are symmetrical;
therefore, the p and n of a given differential pair are inter-
changeable, provided the inversion is consistent across all inputs
and outputs of the AD8191. However, the routing between
inputs and outputs through the AD8191 is fixed. For example,
in quad mode, Output Channel 0 always switches between
Input A0, Input B0, Input C0, Input D0, and so forth.
The AD8191 buffers the TMDS signals and the input traces can
be considered electrically independent of the output traces. In
most applications, the quality of the signal on the input TMDS
traces are more sensitive to the PCB layout. Regardless of the
data being carried on a specific TMDS channel, or whether the
TMDS line is at the input or the output of the AD8191, all four
high speed signals should be routed on a PCB in accordance
with the same RF layout guidelines.
Layout for the TMDS Signals
The TMDS differential pairs can either be microstrip traces,
routed on the outer layer of a board, or stripline traces, routed
on an internal layer of the board. If microstrip traces are used,
there should be a continuous reference plane on the PCB layer
directly below the traces. If stripline traces are used, they must
be sandwiched between two continuous reference planes in the
PCB stack-up. Additionally, the p and n of each differential pair
must have a controlled differential impedance of 100 . The
characteristic impedance of a differential pair is a function of
several variables including the trace width, the distance separating
the two traces, the spacing between the traces and the reference
plane, and the dielectric constant of the PC board binder material.
Interlayer vias introduce impedance discontinuities that can
cause reflections and jitter on the signal path, therefore, it is
preferable to route the TMDS lines exclusively on one layer of the
board, particularly for the input traces. In some applications, such
as using multiple AD8191s to construct large input arrays, the use
of interlayer vias becomes unavoidable. In these situations, the
input termination feature of the AD8191 improves system signal
integrity by absorbing reflections. Take care to use vias minimally
and to place vias symmetrically for each side of a given differential

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 32
pair. Furthermore, to prevent unwanted signal coupling and
interference, route the TMDS signals away from other signals
and noise sources on the PCB.
Both traces of a given differential pair must be equal in length
to minimize intrapair skew. Maintaining the physical symmetry
of a differential pair is integral to ensuring its signal integrity;
excessive intrapair skew can introduce jitter through duty cycle
distortion (DCD). The p and n of a given differential pair should
always be routed together to establish the required 100 differ-
ential impedance. Enough space should be left between the
differential pairs of a given group so that the n of one pair does
not couple to the p of another pair. For example, one technique is
to make the interpair distance 4 to 10 times wider than the
intrapair spacing.
Any group of four TMDS channels (Input A, Input B, Input C,
Input D, or the output) should have closely matched trace
lengths to minimize interpair skew. Severe interpair skew can
cause the data on the four different channels of a group to arrive
out of alignment with one another. A good practice is to match
the trace lengths for a given group of four channels to within
0.05 inches on FR4 material.
The length of the TMDS traces should be minimized to reduce
overall signal degradation. Commonly used PC board material,
such as FR4, is lossy at high frequencies; therefore, long traces
on the circuit board increase signal attenuation resulting in
decreased signal swing and increased jitter through intersymbol
interference (ISI).
Controlling the Characteristic Impedance of a TMDS
Differential Pair
The characteristic impedance of a differential pair depends on
a number of variables including the trace width, the distance
between the two traces, the height of the dielectric material
between the trace and the reference plane below it, and the
dielectric constant of the PCB binder material. To a lesser
extent, the characteristic impedance also depends upon the
trace thickness and the presence of solder mask. There are
many combinations that can produce the correct characteristic
impedance. It is generally required to work with the PC board
fabricator to obtain a set of parameters to produce the desired
results.
One consideration is how to guarantee a differential pair with
a differential impedance of 100 over the entire length of the
trace. One technique to accomplish this is to change the width
of the traces in a differential pair based on how closely one trace
is coupled to the other. When the two traces of a differential
pair are close and strongly coupled, they should have a width
that produces a 100 differential impedance. When the traces
split apart, to go into a connector, for example, and are no
longer so strongly coupled, the width of the traces should be
increased to yield a differential impedance of 100 in the new
configuration.
TMDS Terminations
The AD8191 provides internal, 50 single-ended terminations
for all of its high speed inputs and outputs. It is not necessary to
include external termination resistors for the TMDS differential
pairs on the PCB.
The output termination resistors of the AD8191 back-terminate
the output TMDS transmission lines. These back-terminations
act to absorb reflections from impedance discontinuities on the
output traces, improving the signal integrity of the output traces
and adding flexibility to how the output traces can be routed.
For example, interlayer vias can be used to route the AD8191
TMDS outputs on multiple layers of the PCB without severely
degrading the quality of the output signal.
Auxiliary Control Signals
There are four single-ended control signals associated with each
source or sink in an HDMI/DVI application. These are hot plug
detect (HPD), consumer electronics control (CEC), and two
display data channel (DDC) lines. The two signals on the DDC
bus are SDA and SCL (serial data and serial clock, respectively).
These four signals can be switched through the auxiliary bus of
the AD8191 and do not need to be routed with the same strict
considerations as the high speed TMDS signals.
In general, it is sufficient to route each auxiliary signal as a
single-ended trace. These signals are not sensitive to impedance
discontinuities, do not require a reference plane, and can be
routed on multiple layers of the PCB. However, it is best to
follow strict layout practices whenever possible to prevent the
PCB design from affecting the overall application. The specific
routing of the HPD, CEC, and DDC lines depends upon the
application in which the AD8191 is being used.
For example, the maximum speed of signals present on the
auxiliary lines is 100 kHz I
2
C data on the DDC lines; therefore,
any layout that enables 100 kHz I
2
C to be passed over the DDC
bus should suffice. The HDMI 1.2a specification, however,
places a strict 50 pF limit on the amount of capacitance that can
be measured on either SDA or SCL at the HDMI input connector.
This 50 pF limit includes the HDMI connector, the PCB, and
whatever capacitance is seen at the input of the AD8191, or an
equivalent receiver. There is a similar limit of 100 pF of input
capacitance for the CEC line.
The parasitic capacitance of traces on a PCB increases with
trace length. To help ensure that a design satisfies the HDMI
specification, the length of the CEC and DDC lines on the PCB
should be made as short as possible. Additionally, if there is a
reference plane in the layer adjacent to the auxiliary traces in
the PCB stack-up, relieving or clearing out this reference plane
immediately under the auxiliary traces significantly decreases
the amount of parasitic trace capacitance. An example of the
board stackup is shown in Figure 32.
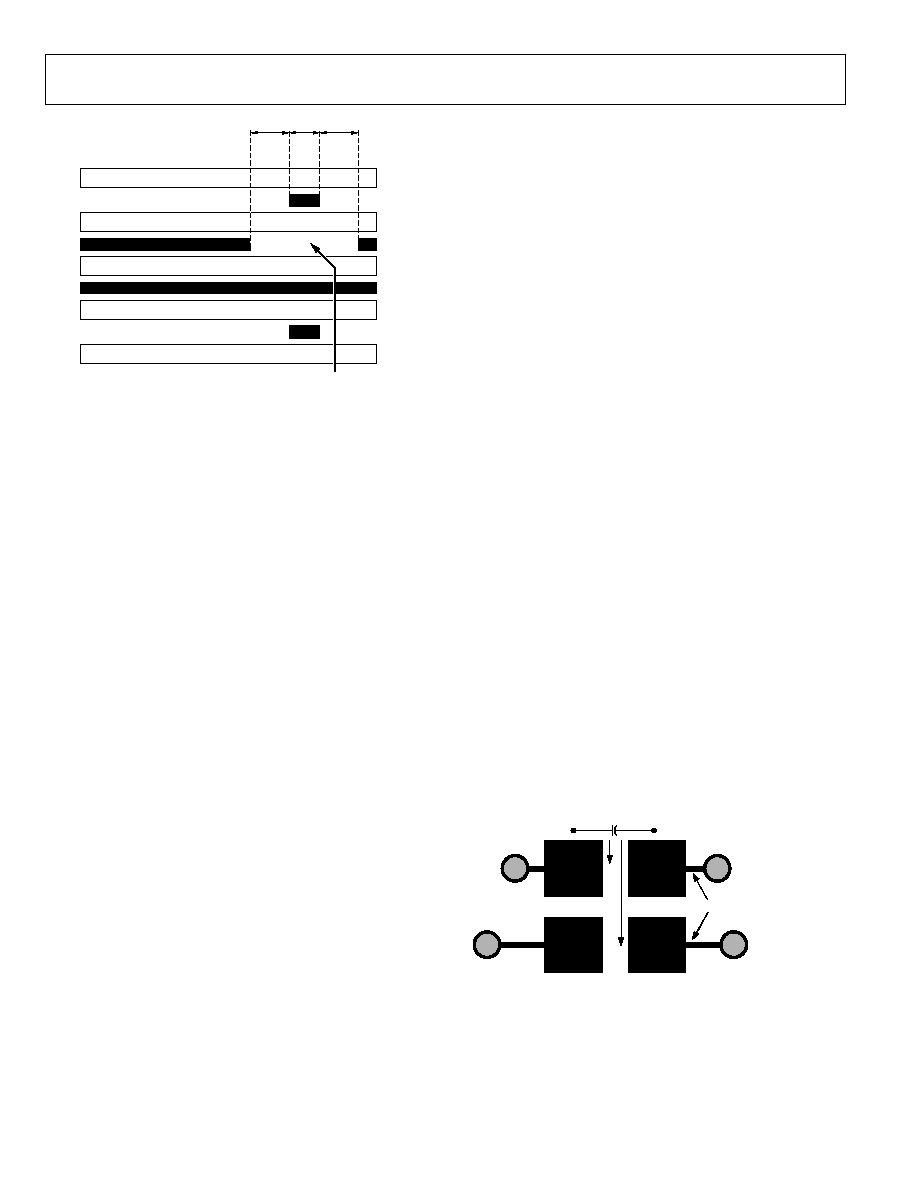
AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 32
PCB DIELECTRIC
LAYER 1: SIGNAL (MICROSTRIP)
SILKSCREEN
SILKSCREEN
PCB DIELECTRIC
PCB DIELECTRIC
LAYER 2: GND (REFERENCE PLANE)
LAYER 3: PWR (REFERENCE PLANE)
LAYER 4: SIGNAL (MICROSTRIP)
W
3W
3W
REFERENCE LAYER
RELIEVED UNDERNEATH
MICROSTRIP
06
12
3-
0
10
Figure 32. Example Board Stackup
HPD is a dc signal presented by a sink to a source to indicate
that the source EDID is available for reading. The placement
of this signal is not critical, but it should be routed as directly
as possible.
When the AD8191 is powered up, one set of the auxiliary in-
puts is passively routed to the outputs. In this state, the AD8191
looks like a 100 resistor between the selected auxiliary inputs
and the corresponding outputs as illustrated in Figure 27. The
AD8191 does not buffer the auxiliary signals, therefore, the
input traces, output traces, and the connection through the
AD8191 all must be considered when designing a PCB to meet
HDMI/DVI specifications. The unselected auxiliary inputs of the
AD8191 are placed into a high impedance mode when the device
is powered up. To ensure that all of the auxiliary inputs of the
AD8191 are in a high impedance mode when the device is powered
off, it is necessary to power the AMUXVCC supply as illustrated
in Figure 28.
In contrast to the auxiliary signals, the AD8191 buffers the
TMDS signals, allowing a PCB designer to layout the TMDS
inputs independently of the outputs.
Power Supplies
The AD8191 has five separate power supplies referenced to
two separate grounds. The supply/ground pairs are:
·
AVCC/AVEE
·
VTTI/AVEE
·
VTTO/AVEE
·
DVCC/DVEE
·
AMUXVCC/DVEE
The AVCC/AVEE (3.3 V) and DVCC/DVEE (3.3 V) supplies
power the core of the AD8191. The VTTI/AVEE supply (3.3 V)
powers the input termination (see Figure 25). Similarly, the
VTTO/AVEE supply (3.3 V) powers the output termination
(see Figure 26). The AMUXVCC/DVEE supply (3.3 V to 5 V)
powers the auxiliary multiplexer core and determines the
maximum allowed voltage on the auxiliary lines. For example,
if the DDC bus is using 5 V I
2
C, then AMUXVCC should be
connected to +5 V relative to DVEE.
In a typical application, all pins labeled AVEE or DVEE should
be connected directly to ground. All pins labeled AVCC,
DVCC, VTTI, or VTTO should be connected to 3.3 V, and
Pin AMUXVCC tied to 5 V. The supplies can also be powered
individually, but care must be taken to ensure that each stage of
the AD8191 is powered correctly.
Power Supply Bypassing
The AD8191 requires minimal supply bypassing. When
powering the supplies individually, place a 0.01 F capacitor
between each 3.3 V supply pin (AVCC, DVCC, VTTI, and
VTTO) and ground to filter out supply noise. Generally, bypass
capacitors should be placed near the power pins and should
connect directly to the relevant supplies (without long inter-
vening traces). For example, to improve the parasitic inductance
of the power supply decoupling capacitors, minimize the trace
length between capacitor landing pads and the vias as shown in
Figure 33.
EXTRA ADDED INDUCTANCE
RECOMMENDED
NOT RECOMMENDED
0
6123-
033
Figure 33. Recommended Pad Outline for Bypass Capacitors

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 29 of 32
In applications where the AD8191 is powered by a single 3.3 V
supply, it is recommended to use two reference supply planes
and bypass the 3.3 V reference plane to the ground reference
plane with one 220 pF, one 1000 pF, two 0.01 F, and one 4.7 F
capacitors. The capacitors should via down directly to the
supply planes and be placed within a few centimeters of the
AD8191. The AMUXVCC supply does not require additional
bypassing. This bypassing scheme is illustrated in Figure 34.
AD8191
AUXILIARY LINES
TMDS TRACES
DECOUPLING
CAPACITORS
06
12
3-
03
4
Figure 34. Example Placement of Power Supply Decoupling Capacitors
Around the AD8191
AD8191
Rev. J | Page 30 of 32
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-026-BED
TOP VIEW
(PINS DOWN)
1
25
26
51
50
75
76
100
0.50
BSC
LEAD PITCH
0.27
0.22
0.17
1.60 MAX
0.75
0.60
0.45
VIEW A
PIN 1
1.45
1.40
1.35
0.15
0.05
0.20
0.09
0.08
COPLANARITY
VIEW A
ROTATED 90° CCW
SEATING
PLANE
7°
3.5°
0°
14.20
14.00 SQ
13.80
16.20
16.00 SQ
15.80
05
17
06
-
A
Figure 35. 100-Lead Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP]
(ST-100)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model
Temperature Range
Package Description
Package Option
Ordering Quantity
AD8191ASTZ
1
-40°C to +85°C
100-Lead Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP]
ST-100
AD8191ASTZ-RL
1
-40°C to +85°C
100-Lead Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP], Reel
ST-100
1,000
AD8191-EVAL
Evaluation
Kit
1
Z = Pb-free part.

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 31 of 32
NOTES

AD8191
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 32
NOTES
Purchase of licensed I
2
C
components of Analog Devices or one of its sublicensed Associated Companies conveys a license for the purchaser under the Philips
I
2
C
Patent Rights to use these components in an I
2
C
system, provided that the system conforms to the I
2
C
Standard Specification as defined by Philips.
©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D06123-0-10/06(0)
Document Outline
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- Thermal Resistance
- Maximum Power Dissipation
- ESD Caution
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- Quad Switching Mode
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- Quad Switching Mode
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- HS_EN: High Speed (TMDS) Channels Enable Bit
- HS_SM[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Switching Mode Select Bus
- HS_CH[3:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Switch Source Select Bus
- þÿ
- AUX_EN: Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switch Enable Bit
- AUX_SM[1:0]: Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switching Mode Select Bus
- AUX_CH[3:0]: Auxiliary (Low Speed) Switch Source Select Bus
- þÿ
- RX_TO: High Speed (TMDS) Channels Input Termination On/Off Select Bit
- þÿ
- RX_PT[X]: High Speed (TMDS) Input Channel X Pulse-On-Source Switch Select Bit
- þÿ
- RX_EQ[X]: High Speed (TMDS) Input X Equalization Level Select Bit
- þÿ
- þÿ
- TX_PTO: High Speed (TMDS) Output Termination On/Off Select Bit (For All Channels)
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- PP_EN: High Speed (TMDS) Channels Enable Bit
- PP_CH[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Switch Source Select Bus
- þÿ
- PP_CH[1:0]: Auxiliary Switch Source Select Bus
- þÿ
- þÿ
- þÿ
- PP_EQ: High Speed (TMDS) Inputs Equalization Level Select Bit (For All TMDS Input Channels)
- þÿ
- PP_PE[1:0]: High Speed (TMDS) Output Pre-Emphasis Level Select Bus (For All TMDS Channels)
- PP_OTO: High Speed (TMDS) Output Termination On/Off Select Bit (For All TMDS Channels)
- PP_OCL: High Speed (TMDS) Output Current Level Select Bit (For All TMDS Channels)
- þÿ
- þÿ































